Friuli-Venezia Giulia
| Friuli-Venezia Giulia | |||
| Flag | Coat of arms | ||
|
|||
| Location | |||
 |
|||
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) | ||
| Administration | |||
| Country | Italy | ||
| NUTS Region | ITD | ||
| Capital | Trieste | ||
| President | Renzo Tondo (PdL) | ||
| Basic statistics | |||
| Area | 7,856 km² (3,033 sq mi) (Ranked 17th, 2.6 %) |
||
| Population | 1,222,061 (12/2007) (Ranked 15th, 2.0 %) |
||
| - Density | 156 /km² (403 /sq mi) | ||
| Other information | |||
| GDP/ Nominal | € 34.3 billion (2006) | ||
| Website | www.regione.fvg.it | ||
Friuli-Venezia Giulia (Friulian: Friûl-Vignesie Julie, German: Friaul-Julisch Venetien, Slovene: Furlanija - Julijska krajina, Venetian: Friul-Venezsia Jułia) is one of the twenty regions of Italy, and one of five autonomous regions with special statute. The capital is Trieste. It has an area of 7,856 km² and about 1.2 million inhabitants. A natural opening to the sea for many Central European countries, the region is traversed by the major transport routes between the east and west of southern Europe. It encompasses two historical regions, each own with its dinstinct identity: Friuli and Venezia Giulia
Contents |
Geography
Located in northeastern Italy, Friuli-Venezia Giulia borders the region of Veneto to the west, the republics of Austria and Slovenia to the north and east, and the Adriatic Sea to the south. Friuli-Venezia Giulia has an area of 7844 km² and 1.2 million inhabitants. The length of its coast is 111.7 km. Its capital is Trieste.
Friuli-Venezia Giulia is divided into four provinces:
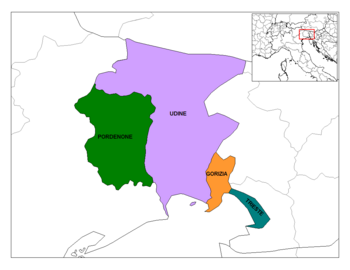
- Gorizia
- Pordenone
- Trieste
- Udine
History
- Main articles: History of Friuli and History of Venezia Giulia
- See also: Gorizia and Gradisca and Austrian Littoral
The name comes from the Latin name of the town of Cividale, ancient capital of the Lombard duchy, which used to be "Forum Iulii" ("Julius' forum", named after Julius Caesar). This region was created after World War II to solve the problem of Trieste, which had lost its natural hinterland, that was the major part of Venezia Giulia and has been included in the then-existing country of Yugoslavia. Therefore it was decided to aggregate the historical region of Friuli to Trieste.
Economy
- See also: Friuli-Venezia Giulia wine
Agricultural products include corn, grapes, sugar beet and cheese. Cattle-breeding is important. Industry is based on the shipyards of Trieste and Monfalcone, the steel factories of Pozzuolo del Friuli, the vineyards that produce wine and grappa. Furniture production is concentrated in Manzano and Brugnera.
Politics
PdL gained 53.8% of Friuli-Venezia Giulia's votes at the Italian general election in 2008. The region's local government, led by President Renzo Tondo, is center-right.
Demographics
Apart from Italian, the Friulian language is spoken in most of the region — with a few exceptions, most notably Trieste; there is also a sizeable Slovenian and a small German minority.
The Slovenian language is spoken throughout the province of Trieste, as well as in the eastern parts of the provinces of Gorizia and Udine and in the area called Venetian Slovenia, which comprises the Resia Valley and in the upper valleys of the rivers Torre and Natisone, with many villages having both Italian and Slovenian names. The number of Slovenes in the province is estimated to be somewhere between 50 000 and 150 000 depending on the source.
The number of native German speakers in Friuli-Venezia Giulia is estimated to be around 2,000. They live in the Channel Valley (municipalities of Tarvisio, Malborghetto Valbruna and Pontebba), which is adjacent to Austria, and in the municipality of Sauris and the frazione of Timau (Tischlbong in the local Germanic language)(municipality of Paluzza), which each form a language exclave.
As of 2006, the Italian national institute of statistics ISTAT estimated that 58,915 foreign-born immigrants live in Friuli-Venezia Giulia, or 4.9% of the total regional population.
Towns of Friuli-Venezia Giulia with a population of 50,000 or more:
| Comune | Population (2006 estimate) |
|---|---|
| Trieste | 206,058 |
| Udine | 96,678 |
| Pordenone | 50,926 |
Notable residents or natives
- Ernesto Illy, Cavaliere del Lavoro (Knight of Industry 1994), Chairman illycaffè S.p.A.
- Dino Zoff, football goalkeeper Italy, Juventus.
- Vladimir Bartol, writer.
- Leo Castelli, art dealer.
- Avgust Černigoj, painter.
- Max Fabiani, architect.
- Tarcisio Burgnich, footballer.
- Arturo Malignani, inventor of the incandescent light bulb.
- Claudio Magris, writer.
- Primo Carnera Boxer.
- Ermes di Colorêt (16th century)
- Saint Paulinus II, (c. 750-802), patriarch of Aquileia
- Pietro Zorutti (19th century)
- Pier Paolo Pasolini (20th century)
- Boris Pahor, writer.
- Umberto Saba, poet.
- Italo Svevo, writer.
- Carlo Michelstaedter, philosopher.
- Fabio Capello, football manager.
- Ludovico Manin, last Doge of Venice
- Mario Agante, poet
External links
- Official site of the Autonomous Region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia
- fvg.INFO
- Map of Friuli-Venezia Giulia
- Tourism Friuli Venezia Giulia
- Airport of Friuli Venezia Giulia
- La Patrie dal Friûl
- Friulian Meteorological Observatory

