Flag of Scotland
 |
|
| Name | Saltire |
| Use | Civil and state flag. |
| Proportion | 1:2, 2:3, 3:5, or 4:5 |
| Adopted | 14th century (approx)[1] |
| Design | White saltire on a blue field |
The Flag of Scotland is a white saltire, a crux decussate (X-shaped cross) representing the cross of the Christian martyr Saint Andrew, the patron saint of Scotland, on a blue field. It is named the Saltire or the Saint Andrew's Cross. In heraldic language, it may be blazoned Azure, a saltire argent.
Contents |
History
According to legend, in 832 A.D. King Óengus (II) (or King Angus) led the Picts and Scots in battle against the Angles under a king named Athelstan near modern-day Athelstaneford in East Lothian. King Angus and his men were surrounded and he prayed for deliverance. During the night Saint Andrew, who was martyred on a saltire cross, appeared to Angus and assured him of victory. On the following morning a white saltire against the background of a blue sky appeared to both sides. The Picts and Scots were heartened by this, but the Angles lost confidence and were defeated. This saltire design has been the Scottish flag ever since.
Material Evidence
Material evidence of the saltire's use dates from somewhat later. The earliest record to the Saint Andrew's cross flag dates from 1165 AD, where reference is made to the 9th Century battle. By 1180 the St. Andrews cross flag is on the seal of St. Andrews. The St. Andrews cross was shown as the national emblem of Scotland on the seal of the guardians of Scotland. In 1385 the Parliament of Scotland decreed that Scottish soldiers should wear the saltire as a distinguishing mark. The earliest surviving Scottish flag consisting solely of the saltire dates from 1503: a white cross on a red background. By 1540 the legend of King Angus had been altered to include the vision of the crux decussata against a blue sky. Thereafter, this saltire design in its present form became the national flag of Scotland.
Flying the flag

Scottish Parliament
There are five flagpoles outside the Scottish Parliament Building in Edinburgh. The Saltire is flown every day, alongside the Union Flag and the EU Flag. The fourth flagpole is used for special occasions such as Commonwealth Day and United Nations Day. The fifth pole is used for the Royal Standard.[2]
Edinburgh Castle
Edinburgh Castle is managed by Historic Scotland, but it still has a military garrison of the British Army. Like all British Army bases, it flies the Union Flag (in ratio 5:3) and the Army flies it every day from the Clock Tower. The Saltire is flown every day at the Half Moon Battery.[3]
The flying of the Union Flag at Edinburgh Castle has sometimes caused controversy. In 2001, a group of 20 Scottish National Party MSPs called for the Union Flag to be replaced by the Saltire.[4]
Scottish Government
The Scottish Government has decreed that the Flag will fly on all its buildings every day from 8am until sunset. An exception is made for "national days". On these days, the Saltire shall be lowered and replaced with the Union Flag. These days are the same as the flag days of the United Kingdom with the exception of 3 September (Merchant Navy Day), which is a specific flag day in Scotland and during which the Red Ensign may also be used.
Another difference with the UK days is that on Saint Andrew's Day, the Union Flag will only be flown if the building has more than one flagpole - the Saltire will not be lowered to make way for the Union Flag if there is only one flagpole.[5] This difference arose after Members of the Scottish Parliament complained that Scotland was the only country in the world that could not fly its national flag on its national day.[6]
Others
There is no need to have planning permission to fly the flag from a vertical flagpole. The Flag can be flown at any time by any individual, company, local authority, hospital or school. In recent years, embassies of the United Kingdom have flown the Saltire to mark St Andrew's Day.
Most local authorities in Scotland fly the Saltire. Glasgow City Council fly the flag from the City Chambers building in George Square [7], while the City of Edinburgh Council fly the flag from their own city chambers. In 2007 Angus Council led by Robert Myles decided to scrap the Saltire and replace it with a new Angus flag. This move led to public outcry across Scotland with more than 7,000 people signing a petition opposing the council's move, leading to a compromise whereby the Angus flag would not replace but be flown alongside the Saltire on Council buildings.[8]

Unusually, the ferry operator Caledonian MacBrayne flies the Saltire as a Jack on vessels which have a bow staff, including when such vessels are underway. The world famous Paddle Steamer Waverley also adopts this practice when operating in and around the Firth of Clyde.
The practice of maritime vessels adopting the Saltire, for use as a jack or courtesy flag, may lead to possible confusion in that the Saltire closely resembles the maritime signal flag M, "MIKE", which is used to indicate "My vessel is stopped and making no way through the water". However, so as to avoid confusion and a possible fine,[9] owners of vessels wishing to display an alternative flag to that of the Saltire have resorted to unofficial use of either the Royal Standard of Scotland or the historic Scottish Red Ensign. Last used by the pre-1707 Royal Scots Navy and merchant marine fleets,[10] the Scottish Red Ensign now appears in the catalogues of several flag manufacturers,[11] due to its increased popularity among private citizens for use on water.[12][13]
Many bodies of the Scottish Government use the flag as a design basis; for example, Safer Scotland's emblem depicts a lighthouse shining beams in a saltire shape onto a blue sky. Other Scottish companies have also used the saltire in similar ways.
Colour and dimensions


At various times throughout history colours as light as sky blue or as dark as navy blue have been used (a selection apparently motivated by which colour of blue dye was available at the time). When incorporated as part of the Union Flag, the navy blue colour used was that of the Blue Ensign belonging to the historic 'Blue Squadron' of the English Royal Navy.
Although this navy blue colour was used specifically for depicting the Union Flag on maritime flags on the basis of durability, it soon became standard on Union Flags, both on land and at sea. This navy blue colour trend was adopted for the Saltire itself by many flag manufacturers, resulting in a variety of shades of blue being depicted on the flag of Scotland ranging from "sky blue" to "royal blue" to "navy blue". Eventually, this situation resulted in calls to standardise the colour of Scotland's national flag.
In 2003, a committee of the Scottish Parliament met to examine a petition that the Scottish Government adopt the Pantone 300 colour as a standard. (Note that this blue is of a lighter shade than the Pantone 280 of the Union Flag.) Having taken advice from a number of sources including the office of the Lord Lyon King of Arms, the committee recommended that the optimum shade of blue for the Saltire should be Pantone 300 (that is, 0, 114, 198 in the RGB colour model, or #0072C6 as hexadecimal web colours). Recent versions of the Saltire have therefore largely converged on this official recommendation.
The flag proportions are not fixed, but is generally taken as 1:2, 2:3, 3:5 or 4:5. The bars in the cross should be 1/5 (i.e., 20%) the width of the flag.
Outwith Scotland

Inverse representations, (blue saltire on a white field), of the Scottish Saltire are also used outwith Scotland. In Canada, an inverse representation of the Saltire, combined with the shield from the Royal Arms of the Kingdom of Scotland, forms the modern flag of the Canadian Province of Nova Scotia, the first colonial venture of the Kingdom of Scotland into the Americas.
In Russia, during the period before and after the Soviet Union, the naval ensign of the Russian Navy has been an inverse representation of the Cross of Saint Andrew. (Saint Andrew is also a patron saint of Russia). The very same Saltire was also flown as the flag of Galicia in Spain until 1891, when Russia requested the Galician flag to be modified in order to avoid confusion between Galician ships and Russian Navy ships. The current Galician flag is actually the original blue-over-white saltire but without one of the arms of the cross.
The U.S. state of Alabama's flag is officially "a crimson cross of St. Andrew on a field of white," but the reference is used only to describe the shape without using the vexillological term saltire as that flag's origins are from either or both of the Confederate Battle Flag or the Cross of Burgundy Flag, both of which have saltires and are associated with the history of that state. Similarly, the Spanish island of Tenerife and the remote Colombian islands of San Andrés and Providencia also use the saltire on their flags. In Poland, the official banner of the city of Kraków, (twinned with Edinburgh), feature the coat if arms of Kraków overlying a white saltire on a blue field. The Dutch municipality of Sint-Oedenrode, named after the Scottish princess Saint Oda, also uses the Saltire as the basis of its flag.
The Scottish Saltire is also used unofficially by students and graduates of Xavier University because of the university's blue and white official colours and the resemblance of the flag to the letter "X". It is also the flag for St. Andrew's Scots School, Argentina (founded in 1838) and its "spinoff" university Universidad de San Andrés.
Incorporation into the Union Flag
The Scottish Saltire and field is one of the key components of the Union Flag.[14] The Union Flag has been used in a variety of forms since 1606,[15] when the flags of the Kingdom of Scotland and Kingdom of England were first merged to symbolise the Union of the Crowns.[16] (The Union of the Crowns having occurred in 1603). In Scotland, the Scots superimposed the white cross of the Scottish Flag over the red cross of England, giving precedence to the Saltire. In England, the crosses were reversed. Indeed, when King James VI of Scotland (now also James I of England) visited Scotland in 1618, he rode under a banner where "the whyte and reid croces are so proportionablie interlaced." This refers to the Scottish version of the Union Flag. See below illustrations. [17] However, following the Acts of Union of 1707, which united the Kingdom of Scotland and the Kingdom of England, the 'English' version of the Union Flag was adopted as the official flag of the unified Kingdom of Great Britain.[18]
From 1801, in order to symbolise the union of the Kingdom of Great Britain with the Kingdom of Ireland, a new design which included the St Patrick's Cross was adopted for the flag of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland.[19] This new design, having remained unchanged following the partition of Ireland in 1921 and creation of the Irish Free State and Northern Ireland, continues to be used as the flag of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.

The Saltire, the flag of Scotland: A white saltire on a blue field. (Shown is the recommended "Pantone 300" shade). |

The Scottish version of the Union Flag was used in Scotland from 1606 to 1707, following the Union of the Crowns. |
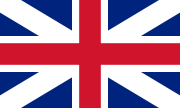
The Union Flag, 1606 (King's Colours), used mostly in England and, from 1707, the flag of the Kingdom of Great Britain. |

Union Flag, 1801, incorporating Cross of Saint Patrick, following Union of Great Britain and Kingdom of Ireland. |
Lion Rampant

The Royal Standard of the King of Scots, also known as the Royal Flag of Scotland or the Lion Rampant, is the flag used historically by the King of Scots. It remains the personal banner of the monarch and use of this flag is restricted under the Act of the Parliament of Scotland 1672 cap. 47 and 30 & 31 Vict. cap. 17.[20]
Despite the legal restrictions concerning the use of this flag, it is often regarded as a second, albeit unofficial, national flag for Scotland, most often seen at sporting events.
See also
- The Bearer of the National Flag of Scotland
- Royal Banner of Scotland
- Royal coat of arms of Scotland
- List of Scottish flags
- List of British flags
- Saint Patrick's Flag
- Saltire
- Flags of Europe
External links
References
- ↑ http://www.saltiresociety.org.uk/name.htm Saltire Society
- ↑ Your Other Questions about the Scottish Parliament questions (last question)
- ↑ Scottish Parliament Written Answers- 11/06/02
- ↑ BBC News- "Political row over flag flying"
- ↑ Scotland.gov.uk- "Royal and ceremonial"/
- ↑ BBC News- "Ministers agree flag day review"
- ↑ britishflags.net- Scotland
- ↑ Forfar Dispatch. URL accessed 05 February 2008.
- ↑ Mail on Sunday article November 25 2007 - partial c/o Highbeam.com Accessed July 24 2008
- ↑ FOTW Accessed July 24 2008
- ↑ The Flag Loft Accessed 24 July 2008
- ↑ Scots Independent - The "Scottish Red Ensign" shown here flying on the Jean de la Lune in Leith Docks, is making a comeback! Accessed July 24 2008
- ↑ Mr Flag Accessed 24 July 2008
- ↑ Scots History Online
- ↑ Royal Website
- ↑ Flag Institute
- ↑ Flags of the World
- ↑ Act of Union (Article 1)
- ↑ Flags of the World
- ↑ "The Lion Rampant"
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
