Eukaryote
| Eukaryotes Fossil range: Proterozoic - Recent |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 Ostreococcus is the smallest known free living eukaryote with an average size of 0.8 µm.
|
||||
| Scientific classification | ||||
|
||||
| Kingdoms | ||||
|
Animalia - Animals
Amoebozoa
Plantae - Plants
Chromalveolata
Rhizaria
Excavata
|
||||
| Alternative phylogeny | ||||
Animals, plants, fungi, and protists are eukaryotes (IPA: /juːˈkærɪɒt/ or IPA: /-oʊt/), organisms whose cells are organized into complex structures enclosed within membranes. The defining membrane-bound structure that differentiates eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus. The presence of a nucleus gives these organisms their name, which comes from the Greek ευ (eu), meaning "good/true," and κάρυον (karyon), "nut." Many eukaryotic cells contain other membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, chloroplasts and Golgi bodies.
Cell division in eukaryotes is different from organisms without a nucleus (prokaryotes). It involves separating the duplicated chromosomes, through movements directed by microtubules. There are two types of division processes. In mitosis, one cell divides to produce two genetically-identical cells. In meiosis, which is required in sexual reproduction, one diploid cell (having two instances of each chromosome, one from each parent) undergoes recombination of each pair of parental chromosomes, and then two stages of cell division, resulting in four haploid cells (gametes). Each gamete has just one complement of chromosomes, each a unique mix of the corresponding pair of parental chromosomes.
Eukaryotes appear to be monophyletic, and so make up one of the three domains of life. The two other domains, bacteria and archaea, are prokaryotes, and have none of the above features. But eukaryotes do share some aspects of their biochemistry with archaea, and so are grouped with archaea in the clade Neomura.
Contents |
Cell features
Eukaryotic cells are typically much larger than prokaryotes. They have a variety of internal membranes and structures, called organelles, and a cytoskeleton composed of microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments, which play an important role in defining the cell's organization and shape. Eukaryotic DNA is divided into several linear bundles called chromosomes, which are separated by a microtubular spindle during nuclear division.
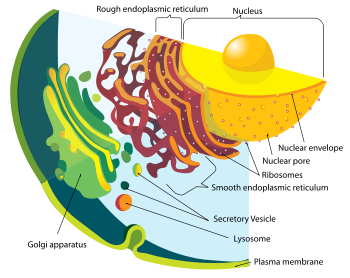
Internal membrane
Eukaryotic cells include a variety of membrane-bound structures, collectively referred to as the endomembrane system. Simple compartments, called vesicles or vacuoles, can form by budding off other membranes. Many cells ingest food and other materials through a process of endocytosis, where the outer membrane invaginates and then pinches off to form a vesicle. It is probable that most other membrane-bound organelles are ultimately derived from such vesicles.
The nucleus is surrounded by a double membrane (commonly referred to as a nuclear envelope), with pores that allow material to move in and out. Various tube- and sheet-like extensions of the nuclear membrane form what is called the endoplasmic reticulum or ER, which is involved in protein transport and maturation. It includes the rough ER where ribosomes are attached, and the proteins they synthesize enter the interior space or lumen. Subsequently, they generally enter vesicles, which bud off from the smooth ER. In most eukaryotes, these protein-carrying vesicles are released and further modified in stacks of flattened vesicles, called Golgi bodies or dictyosomes.
Vesicles may be specialized for various purposes. For instance, lysosomes contain enzymes that break down the contents of food vacuoles, and peroxisomes are used to break down peroxide, which is toxic otherwise. Many protozoa have contractile vacuoles, which collect and expel excess water, and extrusomes, which expel material used to deflect predators or capture prey. In multicellular organisms, hormones are often produced in vesicles. In higher plants, most of a cell's volume is taken up by a central vacuole, which primarily maintains its osmotic pressure.

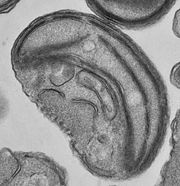
1) Inner membrane
2) Outer membrane
3) Crista
4) Matrix
Mitochondria and plastids
Mitochondria are organelles found in nearly all eukaryotes. They are surrounded by double membranes (known as the phospholipid bi-layer), the inner of which is folded into invaginations called cristae, where aerobic respiration takes place. They contain their own DNA and ribosomes and are only formed by the fission of other mitochondria. They are now generally held to have developed from endosymbiotic prokaryotes, probably proteobacteria. The few protozoa that lack mitochondria have been found to contain mitochondrion-derived organelles, such as hydrogenosomes and mitosomes.
Plants and various groups of algae also have plastids. Again, these have their own DNA and developed from endosymbiotes, in this case cyanobacteria. They usually take the form of chloroplasts, which like cyanobacteria contain chlorophyll and produce energy through photosynthesis. Others are involved in storing food. Although plastids likely had a single origin, not all plastid-containing groups are closely related. Instead, some eukaryotes have obtained them from others through secondary endosymbiosis or ingestion.
Endosymbiotic origins have also been proposed for the nucleus, for which see below, and for eukaryotic flagella, supposed to have developed from spirochaetes. This is not generally accepted, both from a lack of cytological evidence and difficulty in reconciling this with cellular reproduction.
Cytoskeletal structures
Many eukaryotes have long slender motile cytoplasmic projections, called flagella. These are composed mainly of tubulin and shorter cilia, both of which are variously involved in movement, feeding, and sensation. These are entirely distinct from prokaryotic flagella. They are supported by a bundle of microtubules arising from a basal body, also called a kinetosome or centriole, characteristically arranged as nine doublets surrounding two singlets. Flagella also may have hairs, or mastigonemes, and scales connecting membranes and internal rods. Their interior is continuous with the cell's cytoplasm. Microfilamental structures composed by actin and actin binding proteins, e.g., α-actinin, fimbrin, filamin are present in submembraneous cortical layers and bundles, as well. Motor proteins of microtubules, e.g., dynein or kinesin and actin, e.g., myosins provide dynamic character of the network.
Centrioles are often present even in cells and groups that do not have flagella. They generally occur in groups of one or two, called kinetids, that give rise to various microtubular roots. These form a primary component of the cytoskeletal structure, and are often assembled over the course of several cell divisions, with one flagellum retained from the parent and the other derived from it. Centrioles may also be associated in the formation of a spindle during nuclear division.
Significance of cytoskeletal structures is underlined in determination of shape of the cells, as well as their being essential components of migratory responses like chemotaxis and chemokinesis. Some protists have various other microtubule-supported organelles. These include the radiolaria and heliozoa, which produce axopodia used in flotation or to capture prey, and the haptophytes, which have a peculiar flagellum-like organelle called the haptonema.
Plant cell wall
- Further information: Cell wall
Plant cells have a cell wall, a fairly rigid layer outside the cell membrane, providing the cell with structural support, protection, and a filtering mechanism. The cell wall also prevents over-expansion when water enters the cell. The major carbohydrates making up the primary cell wall are cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin. The cellulose microfibrils are linked via hemicellulosic tethers to form the cellulose-hemicellulose network, which is embedded in the pectin matrix. The most common hemicellulose in the primary cell wall is xyloglucan.
Differences between eukaryotic cells
There are many different types of eukaryotic cells, though animals and plants are the most familiar eukaryotes, and thus provide an excellent starting point for understanding eukaryotic structure. Fungi and many protists have some substantial differences, however.
Animal cell
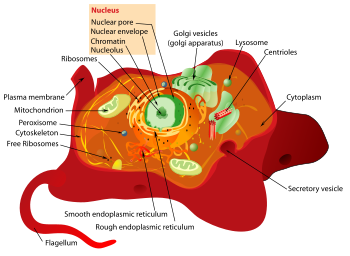
An animal cell is a form of eukaryotic cell that makes up many tissues in animals. The animal cell is distinct from other eukaryotes, most notably plant cells, as they lack cell walls and chloroplasts, and they have smaller vacuoles. Due to the lack of a rigid cell wall, animal cells can adopt a variety of shapes, and a phagocytic cell can even engulf other structures.
There are many different cell types. For instance, there are approximately 210 distinct cell types in the adult human body.
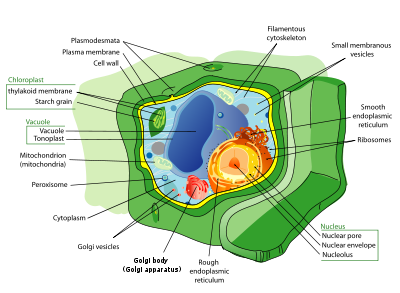
Plant cell
- Further information: Plant cell
Plant cells are quite different from the cells of the other eukaryotic organisms. Their distinctive features are:
- A large central vacuole (enclosed by a membrane, the tonoplast), which maintains the cell's turgor and controls movement of molecules between the cytosol and sap
- A primary cell wall containing cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin, deposited by the protoplast on the outside of the cell membrane; this contrasts with the cell walls of fungi, which contain chitin, and the cell envelopes of prokaryotes, in which peptidoglycans are the main structural molecules
- The plasmodesmata, linking pores in the cell wall that allow each plant cell to communicate with other adjacent cells; this is different from the functionally analogous system of gap junctions between animal cells.
- Plastids, especially chloroplasts that contain chlorophyll, the pigment that gives plants their green color and allows them to perform photosynthesis
- Higher plants, including conifers and flowering plants (Angiospermae) lack the flagellae and centrioles that are present in animal cells.
Fungal cell
Fungal cells are most similar to animal cells, with the following exceptions:
- A cell wall containing chitin
- Less definition between cells; the hyphae of higher fungi have porous partitions called septa, which allow the passage of cytoplasm, organelles, and, sometimes, nuclei. Primitive fungi have few or no septa, so each organism is essentially a giant multinucleate supercell; these fungi are described as coenocytic.
- Only the most primitive fungi, chytrids, have flagella.
Other eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotes are a very diverse group, and their cell structures are equally diverse. Many have cell walls; many do not. Many have chloroplasts, derived from primary, secondary, or even tertiary endosymbiosis; and many do not. Some groups have unique structures, such as the cyanelles of the glaucophytes, the haptonema of the haptophytes, or the ejectisomes of the cryptomonads. Other structures, such as pseudopods, are found in various eukaryote groups in different forms, such as the lobose amoebozoans or the reticulose foraminiferans.
Reproduction
Nuclear division is often coordinated with cell division. This generally takes place by mitosis, a process that allows each daughter nucleus to receive one copy of each chromosome. In most eukaryotes, there is also a process of sexual reproduction, typically involving an alternation between haploid generations, wherein only one copy of each chromosome is present, and diploid generations, wherein two are present, occurring through nuclear fusion (syngamy) and meiosis. There is considerable variation in this pattern, however.
Eukaryotes have a smaller surface to volume area ratio than prokaryotes, and thus have lower metabolic rates and longer generation times. In some multicellular organisms, cells specialized for metabolism will have enlarged surface areas, such as intestinal vili.
Origin and evolution
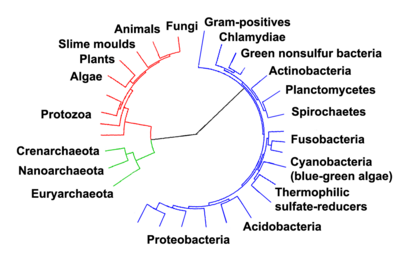
The origin of the eukaryotic cell was a milestone in the evolution of life, since they include all complex cells and almost all multi-cellular organisms. The timing of this series of events is hard to determine; Knoll (2006) suggests they developed approximately 1.6 - 2.1 billion years ago. Some acritarchs are known from at least 1650 million years ago, and the possible alga Grypania has been found as far back as 2100 million years ago. [2] Fossils that are clearly related to modern groups start appearing around 1.2 billion years ago, in the form of a red alga.
Biomarkers suggest that at least stem eukaryotes arose even earlier. The presence of steranes in Australian shales indicates that eukaryotes were present 2.7 billion years ago.[3] [4]
rRNA trees constructed during the 1980s and 1990s left most eukaryotes in an unresolved "crown" group (not technically a true crown), which was usually divided by the form of the mitochondrial cristae; see crown eukaryotes. The few groups that lack mitochondria branched separately, and so the absence was believed to be primitive; but this is now considered an artifact of long-branch attraction, and they are known to have lost them secondarily.[5][6]
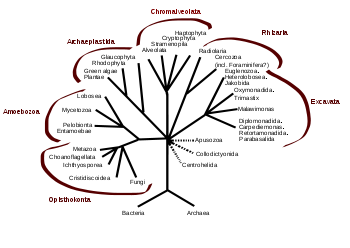
Trees based on actin and other molecules have painted a different and more complete picture. Most eukaryotes are now included in one of the following supergroups, although the relationship between these groups, and the monophyly of each group, is not yet clear:[7][8]
| Opisthokonts | Animals, fungi, choanoflagellates, etc. |
| Amoebozoa | Most lobose amoebae and slime moulds |
| Rhizaria | Foraminifera, Radiolaria, and various other amoeboid protozoa |
| Excavates | Various flagellate protozoa |
| Archaeplastida (or Primoplantae) | Land plants, green algae, red algae, and glaucophytes |
| Chromalveolates | Heterokonts, Haptophytes, Cryptomonads, and Alveolates. |
Several authorities recognize two larger clades, the unikonts and the bikonts, that derive from an ancestral uniflagellar organism and a biflagellate, respectively. In this system, the opisthokonts and amoebozoans are considered unikonts, and the rest bikonts. The chromalveolates were originally thought to be two separate groups, the chromists and the alveolates, but the former was proved to be paraphyletic to the latter, and the two groups combined. Some small protist groups have not been related to any of these supergroups, in particular the centrohelids.
Eukaryotes are closely related to Archaea, at least in terms of nuclear DNA and genetic machinery, and some place them with Archaea in the clade Neomura. In other respects, such as membrane composition, they are similar to eubacteria. Three main explanations for this have been proposed:
- Eukaryotes resulted from the complete fusion of two or more cells, wherein the cytoplasm formed from a eubacterium, and the nucleus from an archaeon,[9] or from a virus.[10][11]
- Eukaryotes developed from Archaea, and acquired their eubacterial characteristics from the proto-mitochondrion.
- Eukaryotes and Archaea developed separately from a modified eubacterium.
|
The origins of the endomembrane system and mitochondria are also unclear.[12] The phagotrophic hypothesis proposes that eukaryotic-type membranes lacking a cell wall originated first, with the development of endocytosis, whereas mitochondria were acquired by ingestion as endosymbionts.[13] The syntrophic hypothesis proposes that the proto-eukaryote relied on the proto-mitochondrion for food, and so ultimately grew to surround it. Here the membranes originated after the engulfment of the mitochondrion, in part thanks to mitochondrial genes (the hydrogen hypothesis is one particular version).[14]
In a study using genomes to construct supertrees, Pisani et al (2007) suggest that, along with evidence that there was never a mitochondrion-less eukaryote, eukaryotes evolved from a syntrophy between an archaea closely related to Thermoplasmatales and an α-proteobacterium, likely a symbiosis driven by sulfur or hydrogen. The mitochondrion and its genome is a remnant of the α-proteobacterial endosymbiont.[15]
See also
- List of sequenced eukaryotic genomes
References
- ↑ Ciccarelli FD, Doerks T, von Mering C, Creevey CJ, Snel B, Bork P (2006). "Toward automatic reconstruction of a highly resolved tree of life". Science 311 (5765): 1283–7. doi:. PMID 16513982.
- ↑ Knoll, Andrew H.; Javaux, E.J, Hewitt, D. and Cohen, P. (2006). "Eukaryotic organisms in Proterozoic oceans". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Part B 361 (1470): 1023–1038. doi:. PMID 16754612. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=1578724.
- ↑ Archean Molecular Fossils and the Early Rise of Eukaryotes, by Jochen Brocks et al., Science, 13 Aug. 1999, pp. 1033-6.
- ↑ Mass extinctions: the microbes strike back by Peter Ward, New Scientist, 9 Feb. 2008, pp. 40-3.
- ↑ Tovar J, Fischer A, Clark CG (1999). "The mitosome, a novel organelle related to mitochondria in the amitochondrial parasite Entamoeba histolytica". Mol. Microbiol. 32 (5): 1013–21. doi:. PMID 10361303.
- ↑ Boxma B, de Graaf RM, van der Staay GW, et al (2005). "An anaerobic mitochondrion that produces hydrogen". Nature 434 (7029): 74–9. doi:. PMID 15744302.
- ↑ Burki F, Shalchian-Tabrizi K, Minge M, Skjæveland Å, Nikolaev SI, et al. (2007). "Phylogenomics Reshuffles the Eukaryotic Supergroups". PLoS ONE 2 (8: e790): e790. doi:.
- ↑ Laura Wegener Parfrey, Erika Barbero, Elyse Lasser, Micah Dunthorn, Debashish Bhattacharya, David J Patterson, and Laura A Katz (2006 December). "Evaluating Support for the Current Classification of Eukaryotic Diversity". PLoS Genet. 2 (12): e220. doi:. PMID 17194223. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1713255.
- ↑ Martin W (December 2005). "Archaebacteria (Archaea) and the origin of the eukaryotic nucleus". Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 8 (6): 630–7. doi:. PMID 16242992.
- ↑ Takemura M (May 2001). "Poxviruses and the origin of the eukaryotic nucleus". J. Mol. Evol. 52 (5): 419–25. doi:. PMID 11443345.
- ↑ Bell PJ (September 2001). "Viral eukaryogenesis: was the ancestor of the nucleus a complex DNA virus?". J. Mol. Evol. 53 (3): 251–6. doi:. PMID 11523012.
- ↑ Jékely G (2007). "Origin of eukaryotic endomembranes: a critical evaluation of different model scenarios". Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 607: 38–51. PMID 17977457.
- ↑ Cavalier-Smith T (March 2002). "The phagotrophic origin of eukaryotes and phylogenetic classification of Protozoa". Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 52 (Pt 2): 297–354. PMID 11931142. http://ijs.sgmjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=11931142.
- ↑ Martin W, Müller M (March 1998). "The hydrogen hypothesis for the first eukaryote". Nature 392 (6671): 37–41. doi:. PMID 9510246.
- ↑ Pisani D, Cotton JA, McInerney JO (2007). "Supertrees disentangle the chimerical origin of eukaryotic genomes". Mol Biol Evol. 24 (8): 1752–60. doi:. PMID 17504772.
- Knoll AH (1992). "The early evolution of eu-karyotes: A geological perspective". Science 256 (5057): 622–27. doi:. PMID 1585174.
- T. Cavalier-Smith (2002). "The phagotrophic origin of eukaryotes and phylogenetic classification of Protozoa". International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 52: 297–354.
- W. Martin & M.J. Russell (1992). "On the origins of cells: a hypothesis for the evolutionary transitions from abiotic geochemistry to chemoautotrophic prokaryotes, and from prokaryotes to nucleated cells". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B.
- S. L. Baldauf (2003). "The Deep Roots of Eukaryotes". Science 300 (5626): 1703–1706. doi:. PMID 12805537.
- Sina M. Adl et al (2005). "The New Higher Level Classification of Eukaryotes with Emphasis on the Taxonomy of Protists". Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology 52 (5): 399. doi:.
This article contains material from the Science Primer published by the NCBI, which, as a U.S. government publication, is in the public domain.