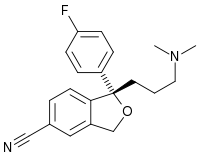
Escitalopram
 |
|
 |
|
|
Escitalopram
|
|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| S-(+)-1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]- 1-(p-fluorophenyl)- 5-phthalancarbonitrileoxalate |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | N06 |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C20H21FN2O |
| Mol. mass | 324.392 g/mol (414.40 as oxalate) |
| SMILES | & |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 80% |
| Protein binding | ~56% |
| Metabolism | Liver, specifically the enzymes CYP3A4 and CYP2C19 |
| Half life | 27–32 hours |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
C |
| Legal status |
℞ Prescription only |
| Routes | Oral |


Escitalopram (trade names Lexapro, Cipralex) is the pure (S) enantiomer of racemic citalopram and is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). Escitalopram is used in the treatment of depression and anxiety.
Contents |
History
Escitalopram was developed in a close cooperation between Lundbeck and Forest Laboratories. Its development was initiated in the summer of 1997, and the resulting new drug application was submitted to the FDA in March 2001. The short time (3.5 years) it took to develop escitalopram can be attributed to the previous extensive experience of Lundbeck and Forest with citalopram, which has similar pharmacology.[1] FDA issued the approval of escitalopram for major depression in August 2002 and for generalized anxiety disorder in December 2003. Escitalopram can be considered an example of "evergreening"[2] - the strategy pharmaceutical companies use in order to extend the lifetime of a drug, in this case of the citalopram franchise. Escitalopram is an enantiomer of citalopram, used for the same indication, and for that reason it required less investment and less time to develop. Two years after escitalopram's launch, when the patent on citalopram expired, the escitalopram sales successfully made up for the loss. On May 23 2006, the FDA approved a generic version of escitalopram by Teva.[3] However, on July 14 of that year, the U.S. District Court of Delaware decided in favor of Lundbeck regarding the patent infringement dispute and ruled the patent on escitalopram valid.[4]
Despite the drugs' similarity, preclinical as well as various clinical studies (including double-blinded studies) have shown differentiated effects of citalopram and escitalopram,[5] as well as a clinical superiority compared with a variety of other SSRIs, such as paroxetine,[6] especially in severely depressed patients, and sertraline. Compared with newer serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors such as venlafaxine[7] and duloxetine[8] escitalopram was shown to be at least as effective.
Pharmacology
Escitalopram (Lexapro by Forest Laboratories in the United States and elsewhere by Lundbeck as Cipralex, Sipralexa and Seroplex)[9] is an antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class. It is approved for the treatment of major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder; other indications include social anxiety disorder, panic disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Escitalopram is the S-stereoisomer (enantiomer) of the earlier Lundbeck drug citalopram (Celexa), hence the name escitalopram. Escitalopram is noted for its high selectivity of serotonin reuptake inhibition and, as a result has fewer side effects not related to its serotonergic activity.[10] Escitalopram acts by increasing intrasynaptic levels of the neurotransmitter serotonin by blocking the reuptake of the neurotransmitter into the neuron. Of the SSRIs currently on the market escitalopram has the highest affinity for the human serotonin transporter (SERT). Another enantiomer of citalopram (R-citalopram) counteracts to a certain degree the serotonin-enhancing action of escitalopram. As a result, escitalopram is a more potent antidepressant than citalopram, which is a mixture of escitalopram and R-citalopram. In order to explain this phenomenon, researchers from Lundbeck proposed that escitalopram enhances its own binding via an additional interaction with another allosteric site on the transporter.[11] Further research by the same group showed that R-citalopram also enhances binding of escitalopram,[12] and therefore the allosteric interaction cannot explain the observed counteracting effect. However, in the most recent paper the same authors again reversed their findings and reported that R-citalopram decreases binding of escitalopram to the transporter.[13] Although allosteric binding of escitalopram to the serotonin transporter is of unquestionable research interest, its clinical relevance is unclear since the binding of escitalopram to the allosteric site is at least 1000 times weaker than to the primary binding site.
In vitro studies using human liver microsomes indicated that CYP3A4 and CYP2C19 are the primary isozymes involved in the N-demethylation of escitalopram.
Side effects and drug interactions
The side effect profile of escitalopram is close to that of other SSRIs, with nausea, somnolence, and gastrointestinal side effects reported as relatively common. Escitalopram, like other SSRIs[14], has been shown to cause sexual side effects in many patients. Escitalopram is not associated with significant weight gain. For example, 0.6 kg mean weight change after 6 months of treatment with escitalopram for depression was insignificant and similar to that with placebo (0.2 kg).[15] 1.4-1.8 kg mean weight gain was reported in 8-month trials of escitalopram for depression,[16] and generalized anxiety disorder.[17] A 52-week trial of escitalopram for the long-term treatment of depression in elderly also found insignificant 0.6 kg mean weight gain.[18] Escitalopram may help reduce weight in those treated for binge eating associated obesity.[19] It may also cause dizziness after exercise in children.
A meta-analysis of clinical trials database conducted by the escitalopram manufacturer Lundbeck found no indication that escitalopram would provoke suicidal behaviour compared with placebo in patients with major depressive disorder and anxiety disorders, on the contrary, suicidal thoughts in the escitalopram group were significantly decreased.[20] An analysis conducted by the FDA found a statistically insignificant 1.5 to 2.4-fold, depending on the statistical technique used, increase of suicidality among the adults treated with escitalopram for psychiatric indications.[21][22][23] Similarly, the UK MHRA data indicate an 80% increase of suicide-related events, not reaching statistical significance, in the escitalopram vs placebo patients.[24] The authors of a related study note the general problem with statistical approaches—due to the rarity of suicidal events in clinical trials, it is hard to draw firm conclusions with a sample smaller than two million patients.[25] A single case report described a patient developing suicidal ideation after beginning treatment with escitalopram, and suicidal ideation disappearing after stopping the treatment.[26]
Escitalopram should be taken with caution when using St John's wort.[27]
Discontinuation symptoms
Escitalopram discontinuation, particularly abruptly, may cause certain withdrawal symptoms such as "electric shock" sensations (also known as "brain shivers" or "brain zaps"), dizziness and irritability.[28]
Footnotes
- ↑ "2000 Annual Report. p 28 and 33" (PDF). Lundbeck (2000). Retrieved on 2007-04-07.
- ↑ "New drugs from old. Presented at the Medical Journal Club, Morriston Hospital by Scott Pegler, Pharmacist at the National Health Service (UK) on November 20, 2006" (PPT). Retrieved on 2007-04-07.
- ↑ Miranda Hitti. "FDA OKs Generic Depression Drug -- Generic Version of Lexapro Gets Green Light", WebMD. Retrieved on 2007-10-10.
- ↑ Marie-Eve Laforte (2006-07-14). "US court upholds Lexapro patent", FirstWord. Retrieved on 2007-10-10.
- ↑ Moore N, Verdoux H, Fantino B (2005). "Prospective, multicentre, randomized, double-blind study of the efficacy of escitalopram versus citalopram in outpatient treatment of major depressive disorder". International Clinical Psychopharmacology 20 (3): 131–137. doi:. PMID 15812262.
- ↑ Boulenger JP, Huusom AK, Florea I, Baekdal T, Sarchiapone M (2006). "A comparative study of the efficacy of long-term treatment with escitalopram and paroxetine in severely depressed patients". Current Medical Research and Opinion 22 (7): 1331–41. doi:. PMID 16834832.
- ↑ Bielski RJ, Ventura D, Chang CC (2004). "A double-blind comparison of escitalopram and venlafaxine extended release in the treatment of major depressive disorder". The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 65 (9): 1190–1196. PMID 15367045.
- ↑ Nierenberg AA, Greist JH, Mallinckrodt CH, et al (2007). "Duloxetine versus escitalopram and placebo in the treatment of patients with major depressive disorder: onset of antidepressant action, a non-inferiority study". Current Medical Research and Opinion 23 (2): 401–416. doi:. PMID 17288694.
- ↑ "Cipralex". Lundbeck. Retrieved on 2008-01-03.
- ↑ Burke WJ, Kratochvil CJ (2002). "Stereoisomers in Psychiatry: The Case of Escitalopram" (PDF). Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry 4 (1): 20–24. PMID 15014731. http://www.psychiatrist.com/pcc/pccpdf/v04n01/v04n0107.pdf.
- ↑ For the overview of supporting data, see Sánchez C, Bøgesø KP, Ebert B, Reines EH, Braestrup C (2004). "Escitalopram versus citalopram: the surprising role of the R-enantiomer". Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 174 (2): 163–76. doi:. PMID 15160261.
- ↑ Chen F, Larsen MB, Sánchez C, Wiborg O (2005). "The S-enantiomer of R,S-citalopram, increases inhibitor binding to the human serotonin transporter by an allosteric mechanism. Comparison with other serotonin transporter inhibitors". European Neuropsychopharmacology 15 (2): 193–198. doi:. PMID 15695064.
- ↑ Mansari ME, Wiborg O, Mnie-Filali O, Benturquia N, Sánchez C, Haddjeri N (2007). "Allosteric modulation of the effect of escitalopram, paroxetine and fluoxetine: in-vitro and in-vivo studies". The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 10 (1): 31–40. doi:. PMID 16448580.
- ↑ Clayton A, Keller A, McGarvey EL (2006). "Burden of phase-specific sexual dysfunction with SSRIs". Journal of Affective Disorders 91 (1): 27–32. doi:. PMID 16430968.
- ↑ Baldwin DS, Reines EH, Guiton C, Weiller E (2007). "Escitalopram therapy for major depression and anxiety disorders". Ann Pharmacother 41 (10): 1583–92. doi:. PMID 17848424.
- ↑ Pigott TA, Prakash A, Arnold LM, Aaronson ST, Mallinckrodt CH, Wohlreich MM (2007). "Duloxetine versus escitalopram and placebo: an 8-month, double-blind trial in patients with major depressive disorder". Curr Med Res Opin 23: 1303. doi:. PMID 17559729.
- ↑ Davidson JR, Bose A, Wang Q (2005). "Safety and efficacy of escitalopram in the long-term treatment of generalized anxiety disorder". J Clin Psychiatry 66 (11): 1441–6. PMID 16420082.
- ↑ Kasper S, Lemming OM, de Swart H (2006). "Escitalopram in the long-term treatment of major depressive disorder in elderly patients". Neuropsychobiology 54 (3): 152–9. doi:. PMID 17230032.
- ↑ Guerdjikova, Anna I.; Susan L. McElroy, Renu Kotwal, Jeffrey A. Welge, Erik Nelson, Katie Lake, David D' Alessio, Paul E. Keck Jr, James I. Hudson (2008). "High-dose escitalopram in the treatment of binge-eating disorder with obesity: a placebo-controlled monotherapy trial". Human Psychopharmacology: Clinical and Experimental 23 (1): 1–11. doi:. PMID 18058852.
- ↑ Pedersen AG (2005). "Escitalopram and suicidality in adult depression and anxiety". International Clinical Psychopharmacology 20 (3): 139–143. doi:. PMID 15812263.
- ↑ Levenson M, Holland C. "Antidepressants and Suicidality in Adults: Statistical Evaluation. (Presentation at Psychopharmacologic Drugs Advisory Committee; December 13, 2006)". Retrieved on 2007-05-13.
- ↑ Stone MB, Jones ML (2006-11-17). "CLINICAL REVIEW: RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN ANTIDEPRESSANT DRUGS AND SUICIDALITY IN ADULTS" (PDF). Overview for December 13 Meeting of Psychopharmacologic Drugs Advisory Committee (PDAC) 11-74. FDA. Retrieved on 2007-09-22.
- ↑ Levenson M, Holland C (2006-11-17). "Statistical Evaluation of Suicidality in Adults Treated with Antidepressants" (PDF). Overview for December 13 Meeting of Psychopharmacologic Drugs Advisory Committee (PDAC) 75-140. FDA. Retrieved on 2007-09-22.
- ↑ Gunnell D, Saperia J, Ashby D (2005). "Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and suicide in adults: meta-analysis of drug company data from placebo controlled, randomised controlled trials submitted to the MHRA's safety review". BMJ 330 (7488): 385. doi:. PMID 15718537.
- ↑ Khan A, Schwartz K (2007). "Suicide risk and symptom reduction in patients assigned to placebo in duloxetine and escitalopram clinical trials: analysis of the FDA summary basis of approval reports". Ann Clin Psychiatry 19 (1): 31–6. doi:. PMID 17453659.
- ↑ Budur, Kumar; Jeffrey Hutzler (June 2004). "Severe suicidal ideation with escitalopram (Lexapro): a case report". Primary Care Psychiatry 9 (2): 67–68. doi:.
- ↑ Karch, Amy (2006). 2006 Lippincott's Nursing Drug Guide. Philadephia, Baltimore, New York, London, Buenos Aires, Hong Kong, Sydney, Tokyo: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 1-58255-436-6.
- ↑ "Lexapro -- Warnings". RxList (12/08/2004). Retrieved on 2006-10-22.
External links
- Lexapro (Forest Laboratories) Official Lexapro Homepage
- Cipralex (Lundbeck) Official Cipralex Homepage
- Pharmacological information Lexapro
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||