Fly
| Flies Fossil range: Middle Triassic - Recent |
||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 A poster with sixteen different species of flies
|
||||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
| Suborders | ||||||||||||||
|
Nematocera (includes Eudiptera) |
True flies are insects of the Order Diptera (Greek: di = two, and pteron = wing), possessing a single pair of wings on the mesothorax and a pair of halteres, derived from the hind wings, on the metathorax.
The presence of a single pair of wings distinguishes true flies from other insects with "fly" in their name, such as mayflies, dragonflies, damselflies, stoneflies, whiteflies, fireflies, alderflies, dobsonflies, snakeflies, sawflies, caddisflies, butterflies or scorpionflies. Some true flies have become secondarily wingless, especially in the superfamily Hippoboscoidea, or among those that are inquilines in social insect colonies.
It is a large order, containing an estimated 240,000 species of mosquitos, gnats, midges and others, although under half of these (about 120,000 species) have been described [1]. It is one of the major insect orders both in terms of ecological and human (medical and economic) importance. The Diptera, in particular the mosquitoes (Culicidae), are of great importance as disease transmitters, acting as vectors for malaria, dengue, West Nile virus, yellow fever, encephalitis and other infectious diseases.
Contents |
Classification
- See also: List of families of Diptera

There are two generally accepted suborders of Diptera. The Nematocera are usually recognized by their elongated bodies and feathery antennae as represented by mosquitoes and crane flies. The Brachycera tend to have a more roundly proportioned body and very short antennae. A more recent classification has been proposed in which the Nematocera is split into two suborders, the Archidiptera and the Eudiptera, but this has not yet gained widespread acceptance among dipterists.
- Suborder Nematocera (77 families, 35 of them extinct) – long antennae, pronotum distinct from mesonotum. In Nematocera, larvae are either eucephalic or hemicephalic and often aquatic.
- Suborder Brachycera (141 families, 8 of them extinct) – short antennae, the pupa is inside a puparium formed from the last larval skin. Brachycera are generally robust flies with larvae having reduced mouthparts.
- Infraorders Tabanomorpha and Asilomorpha – these comprise the majority of what was the Orthorrhapha under older classification schemes. The antennae are short, but differ in structure from those of the Muscomorpha.
- Infraorder Muscomorpha – (largely the Cyclorrhapha of older schemes). Muscomorpha have 3-segmented, aristate (with a bristle) antennae and larvae with three instars that are acephalic (maggots).
Most of the Muscomorpha are further subdivided into the Acalyptratae and Calyptratae based on whether or not they have a calypter (a wing flap that extends over the halteres).
Beyond that, considerable revision in the taxonomy of the flies has taken place since the introduction of modern cladistic techniques, and much remains uncertain. The secondary ranks between the suborders and the families are more out of practical or historical considerations than out of any strict respect for phylogenetic classifications (some modern cladists tend to spurn the use of Linnaean rank names). Nearly all classifications in use now, including this article, contain some paraphyletic groupings; this is emphasized where the numerous alternative systems are most greatly at odds. See list of families of Diptera.
Dipterans belong to the group Mecopterida, that also contains Mecoptera, Siphonaptera, Lepidoptera (butterflies and moths) and Trichoptera. Inside it, they are sometimes classified closely together with Mecoptera and Siphonaptera in the superorder Antliophora [2].
Evolution
Diptera are usually thought to derive from Mecoptera or a strictly related group. First true dipterans are known from the Middle Triassic, becoming widespread during the Middle and Late Triassic [3].
Flies in culture
Flies have often been used in mythology and literature to represent agents of death and decay, such as the Biblical fourth plague of Egypt, or portrayed as nuisances (e.g., in Greek mythology, Myiagros was a god who chased away flies during the sacrifices to Zeus and Athena, and Zeus sent a fly to bite the horse Pegasus causing Bellerophon to fall back to Earth when he attempted to ride to Mount Olympus), though in a few cultures the connotation is not so negative (e.g., in the traditional Navajo religion, Big Fly is an important spirit being). Emily Dickinson's poem "I Heard a Fly Buzz When I Died" also makes reference to flies in the context of death.
Not surprisingly, in art and entertainment, flies are also used primarily to introduce elements of horror or the simply mundane; an example of the former is the 1958 science fiction film The Fly (remade in 1986), in which a scientist accidentally exchanges parts of his body with those of a fly. Examples of the latter include trompe l'oeil paintings of the fifteenth century such as Portrait of a Carthusian by Petrus Christus, showing a fly sitting on a fake frame [4], a 2001 art project by Garnet Hertz in which a complete web server was implanted into a dead fly[1], and various musical works (such as Yoko Ono's album Fly, U2's song "The Fly," Dave Matthews' song "The Fly" and Béla Bartók's "From the Diary of a Fly"). The ability of flies to cling to almost any surface has also inspired the title of Human Fly for stunt performers whose stunts involve climbing buildings, including both real life and fictional individuals.
Aside from the fictional and conceptual role flies play in culture, there are practical roles that flies can play (e.g., flies are reared in large numbers in Japan to serve as pollinators of sunflowers in greenhouses), especially the maggots of various species.
Maggots
- Further information: Maggot
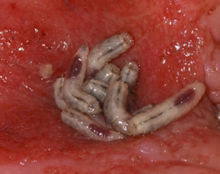
Some types of maggots found on corpses can be of great use to forensic scientists. By their stage of development, these maggots can be used to give an indication of the time elapsed since death, as well as the place the organism died. Maggot species can be identified through the Use of DNA in forensic entomology. The size of the house fly maggot is 10–20 mm (⅜–¾ in). At the height of the summer season, a generation of flies (egg to adult) may be produced in 12–14 days.
Other types of maggots are bred commercially, as a popular bait in angling, and a food for carnivorous pets such as reptiles or birds.
Maggots have been used in medicine to clean out necrotic wounds [5], and in food production, particularly of cheeses (casu marzu).
Gallery
References
- ↑ B. M. Wiegmann & D. K. Yeates (1996). "Tree of Life: Diptera".
- ↑ "Taxon: Superorder Antliophora". The Taxonomicon. Retrieved on 2007-08-21.
- ↑ V. A. Blagoderov, E. D. Lukashevich & M. B. Mostovski (2002). "Order Diptera Linné, 1758. The true flies". in A. P. Rasnitsyn & D. L. J. Quicke. History of Insects. Kluwer Academic Publishers. ISBN 1-4020-0026-X. http://palaeoentomolog.ru/New/diptera.html.
- ↑ "Portrait of a Carthusian, 1446". Timeline of Art History. The Metropolitan Museum of Art (October 2006).
- ↑ Ronald A. Sherman, MD, MSC, University of California (1998)©. "Maggot use of necrotic wounds".
Biology
- Harold Oldroyd The Natural History of Flies. New York: W. W. Norton.1965.
- Eugène Séguy Diptera: recueil d'etudes biologiques et systematiques sur les Dipteres du Globe (Collection of biological and systematic studies on Diptera of the World). 11 vols. Text figs. Part of Encyclopedie Entomologique, Serie B II: Diptera. 1924-1953.
- Eugène Seguy. La Biologie des Dipteres 1950. pp. 609. 7 col + 3 b/w plates, 225 text figs.
Classification
- Colless, D.H. & McAlpine, D.K.1991 Diptera (flies) , pp. 717-786. In: The Division of Entomology. Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation, Canberra (spons.), The insects of Australia.Melbourne Univ. Press, Melbourne.
- Griffiths, G.C.D. The phylogenetic classification of Diptera Cyclorrhapha, withspecial reference to the structure of the male postabdomen. Ser. Ent. 8, 340 pp. [Dr. W. Junk, N. V., The Hague] (1972).
- Willi Hennig Die Larvenformen der Dipteren. 3. Teil. Akad.-Verlag, Berlin. 185 pp., 3 pls. 1948
- Willi Hennig (1954) Flugelgeader und System der Dipteren unter Berucksichtigung der aus dem Mesozoikum beschriebenen Fossilien. Beitr. Ent. 4: 245-388 (1954).
- F. Christian Thompson. "Sources for the Biosystematic Database of World Diptera (Flies)" (PDF). United States Department of Agriculture, Systematic Entomology Laboratory.
- Willi Hennig: Diptera (Zweifluger). Handb. Zool. Berl. 4 (2 ) (31):1-337. General introduction with key to World Families. In German.
Evolution
- Blagoderov, V.A., Lukashevich, E.D. & Mostovski, M.B. 2002. Order Diptera. In: Rasnitsyn, A.P. and Quicke, D.L.J. The History of Insects, Kluwer Publ., Dordrecht, Boston, London, pp. 227-240.
External links
- The Diptera Site
- The Bishop Museum Catalog of Fossil Diptera
- The Tree of Life Project
- Diptera at the Open Directory Project
- Dipterists Forum - The society of British Dipterists
- [2] Dipterists Forum Wiki
- Flies United States Environmental Protection Agency and University of Florida/Institute of Food and Agricultural SciencesS National Public Health Pesticide Applicator Training Manual