Cyclades
| Cyclades Prefecture Νομός Κυκλάδων |
|
|---|---|
 |
|

|
|
| Country: | |
| Capital: | Ermoupoli |
| Periphery: | South Aegean |
| Population: | 119,549 (2005)Ranked 29th |
| Area: | 2,572 km² (993 sq.mi.) Ranked 23rdh |
| Density: | 46 /km² (120 /sq.mi.) |
| Number of provinces: | 9 |
| Number of municipalities: | 20 |
| Number of communities: | 11 |
| Postal codes: | 84x xx |
| Area codes: | 228x0 |
| Licence plate code: | ΕΜ |
| ISO 3166-2 code: | GR-82 |
The Cyclades (Greek: Κυκλάδες, IPA: [kʲikˈlaðe̞s]) are a Greek island group in the Aegean Sea, south-east of the mainland of Greece; and an administrative prefecture of Greece. They are one of the island groups which constitute the Aegean archipelago. The name refers to the islands around (κυκλάς) the sacred island of Delos. The Cyclades is where the native Greek breed of cat (the Aegean cat) first came from.
The Cyclades comprise about 220 islands, the major ones being Amorgos, Anafi, Ándros, Antiparos, Delos, Eschati, Ios, Kéa, Kimolos, Kythnos, Mílos, Mykonos, Náxos, Páros, Folegandros, Serifos, Sifnos, Sikinos, Síros, Tínos, and Santorini. Most of the smaller islands are uninhabited.
Ermoupolis, on Síros, is the chief town and administrative center of the prefecture.
The islands are peaks of a submerged mountainous terrain, with the exception of two volcanic islands, Milos and Santorini (Thera). The climate is generally dry and mild, but with the exception of Naxos the soil is not very fertile: agricultural produce includes wine, fruit, wheat, olive oil, and tobacco. Cooler temperatures are in higher elevations and mainly do not receive wintry weather. In transportation, the Cyclades is the only prefecture in Greece that is not linked with a state-maintained highway or a highway number. All of the roads in the island complex are secondary or provincial.
Contents |
History

The significant Late Neolithic and Early Bronze Age Cycladic culture is best known for its schematic flat female idols carved out of the islands' pure white marble centuries before the great Middle Bronze Age ("Minoan") culture arose in Crete, to the south: these figures have been looted from burials to satisfy a thriving Cycladic antiquities market since the early 20th century.
A distinctive Neolithic culture amalgamating Anatolian and mainland Greek elements arose in the western Aegean before 4000 BCE, based on emmer wheat and wild-type barley, sheep and goats, pigs, and tuna that were apparently speared from small boats (Rutter). Excavated sites include Saliagos and Kephala (on Keos) with signs of copper-working, Each of the small Cycladic islands could support no more than a few thousand people, though Late Cycladic boat models show that fifty oarsmen could be assembled from the scattered communities (Rutter), and when the highly organized palace-culture of Crete arose, the islands faded into insignificance, with the exception of Delos, which retained its archaic reputation as a sanctuary through the period of Classical Greek civilization.
Archaeology
The first archaeological excavations of the 1880s were followed by systematic work by the British School at Athens and by Christos Tsountas, who investigated burial sites on several islands in 1898 - 1899 and coined the term "Cycladic civilization". Interest lagged, then picked up in the mid-20th century, as collectors competed for the modern-looking figures that seemed so similar to sculpture by Jean Arp or Constantin Brâncuşi. Sites were looted and a brisk trade in forgeries arose. The context for many of these Cycladic figurines has been mostly destroyed and their meaning may never be completely understood. Another intriguing and mysterious object is that of the Cycladic frying pans. More accurate archaeology has revealed the broad outlines of a farming and seafaring culture that had immigrated from Asia Minor ca 5000 BCE. Early Cycladic culture evolved in three phases, between ca 3300 - 2000 BCE, when it was increasingly swamped in the rising influence of Minoan Crete. The culture of mainland Greece contemporary with Cycladic culture is termed Helladic.
In recent decades the Cyclades islands have become popular with European and other tourists, and as a result there have been problems with erosion, pollution, and water shortages.
Area codes
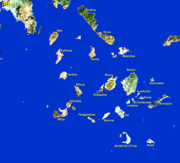
- 22810 - Syros, including Kythnos, Serifos and Syros islands
- 22820 - Andros
- 22830 - Tinos
- 22840 - Paros and Sifnos islands
- 22850 - Amorgos and Naxos islands
- 22860 - Folegandros, Ios, Santorini and Sikinos islands
- 22870 - Kimolos and Milos
- 22880 - Kea Island
- 22890 - Mykonos
Municipalities and communities
| Municipality | YPES code | Seat (if different) | Postal code | Area code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amorgos | 3101 | 840 08 | 22850-2 | |
| Andros | 3103 | 845 00 | 22820-2 | |
| Ano Syros | 3105 | 841 00 | 22810-8 | |
| Drymalia | 3107 | Chalkeio Naxou | 843 02 | 22850 |
| Ermoupoli | 3109 | 841 00 | 22810-2 | |
| Exomvourgo | 3108 | Kampos | 842 00 | 22850-5 |
| Ios | 3112 | 840 01 | 22860-9 | |
| Kea | 3113 | Ioulis | 840 02 | 22880-2 |
| Korthio | 3115 | Ormos Korthiou | 845 02 | 22820-6 |
| Kythnos | 3117 | 840 06 | 22810-3 | |
| Milos | 3118 | 848 00 | 22870-2 | |
| Mykonos | 3119 | 846 00 | 22890-2 | |
| Naxos | 3120 | 843 00 | 22850-2 | |
| Paros | 3123 | 844 00 | 22840-2 | |
| Poseidonia | 3124 | 841 00 | 22810-4 | |
| Santorini | 3111 | 847 00 | 22860-2 | |
| Serifos | 3125 | 840 02 | 22810-5 | |
| Sifnos | 3127 | 840 03 | 22840-3 | |
| Tinos | 3129 | 842 00 | 22830-2 | |
| Ydrousa | 3130 | Gavrio | 845 01 | 22820-7 |
| Community | YPES code | Seat (if different) | Postal code | Area code |
| Anafi | 3102 | 840 09 | 22860-6 | |
| Antiparos | 3104 | 840 07 | 22840-6 | |
| Donousa | 3106 | 843 00 | 22850-5 | |
| Folegandros | 3131 | 840 11 | 22860 | |
| Irakleia | 3110 | 843 00 | 22870-7 | |
| Kimolos | 3114 | 840 04 | 22870-5 | |
| Koufonisi | 3116 | 843 00 | 22870-7 | |
| Oia | 3121 | 847 02 | 22860-7 | |
| Panormos | 3122 | 842 01 | 22830-3 | |
| Schoinoussa | 3128 | 843 00 | 22870-7 | |
| Sikinos | 3126 | 840 10 | 22860-5 |
Provinces
- Province of Andros - Andros
- Province of Tinos - Tinos
- Province of Syros - Ermoupoli
- Province of Kea - Ioulis
- Province of Milos - Milos
- Province of Paros - Paroikia
- Province of Naxos - Naxos
- Province of Amorgos - Amorgos
- Province of Thera - Thera
Note: Provinces no longer hold any legal status in Greece.
See also: List of settlements in the Cyclades prefecture
See also
Further reading
- J. A. MacGillivray and R. L. N. Barber, editors, The Prehistoric Cyclades (Edinburgh) 1984.
- R. L. N. Barber, The Cyclades in the Bronze Age (Iowa City) 1987.
External links
- Cyclades travel guide from Wikitravel
- Jeremy B. Rutter, "The Prehistoric Archaeology of the Aegean" : especially Lessons 2 and 4: chronology, history, bibliography
- Cyclades News portal: Cyclades News portal
|
|||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
