Coccus

Cocci (singular - coccus, from the Latin coccinus (scarlet) and derived from the Greek kokkos (berry) ) are any microorganism (usually bacteria)[1] whose overall shape is spherical or nearly spherical.[2] Describing a bacterium as a coccus, or sphere, distinguishes it from bacillus, or rod. This is the first of many taxonomic traits for identifying and classifying a bacterium according to binomial nomenclature.
Contents |
Aggregations
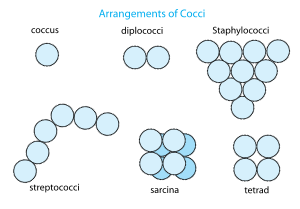
Aggregations of coccoid bacteria often occur and these forms have specific names as well[3]; listed here are the basic forms as well as representative bacterial genera:
- pairs, or diplococci (Neisseria)
- groups of four or eight known as tetrads or sarcina (Micrococci)
- bead-like chains, or streptococci (Streptococcus)
- grapelike clusters, or staphylococci (Staphylococcus)
Clinical significance
Important human pathogens caused by coccoid bacteria include staphylococci infections, some types of food poisoning, some urinary tract infections, toxic shock syndrome, gonorrhea, as well as some forms of meningitis, throat infections, pneumonias, and sinusitis.[4]
References
- ↑ coccus at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ↑ Madigan M; Martinko J (editors). (2005). Brock Biology of Microorganisms (11th ed. ed.). Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-144329-1.
- ↑ Salton MRJ, Kim KS (1996). Structure. In: Baron's Medical Microbiology (Baron S et al, eds.) (4th ed. ed.). Univ of Texas Medical Branch. (via NCBI Bookshelf) ISBN 0-9631172-1-1.
- ↑ Ryan KJ; Ray CG (editors) (2004). Sherris Medical Microbiology (4th ed. ed.). McGraw Hill. ISBN 0-8385-8529-9.
External links
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||