Carpus
| Bone: Carpus | |
|---|---|
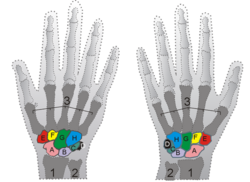 |
|
| BONES OF HAND Proximal: A=Scaphoid, B=Lunate, C=Triquetral, D=Pisiform Distal: E=Trapezium, F=Trapezoid, G=Capitate, H=Hamate |
|
| Latin | ossa carpi |
| Gray's | subject #54 221 |
| MeSH | Carpal+Bones |
| Dorlands / Elsevier |
Carpus |
In tetrapods, the carpus is the sole cluster of the bones in the wrist between the radius and ulna and the metacarpus. The bones of the carpus do not belong to individual fingers (or toes in quadrupeds), whereas those of the metacarpus do. The corresponding part of the foot is the tarsus. Carpal bones are not considered part of the hand but are part of the wrist. The carpal bones allow the wrist to move and rotate vertically and horizontally.
In crustaceans, "carpus" is the scientific term for the claws or "pincers" present on some legs.
Contents |
Variations
In some macropods, the scaphoid and lunar bones are fused into the scaphollunar bone.[1]
The carpus
| Row | Name | Proximal/radial articulations | Distal articulations | Metacarpal articulations |
| Proximal | Scaphoid | radius, lunate | trapezium, trapezoid, capitate | - |
| Proximal | Lunate | radius, scaphoid, triquetral | capitate, hamate | - |
| Proximal | Triquetral | lunate, pisiform (but NOT ulna) | hamate | - |
| Proximal | Pisiform (sesamoid bone) | triquetral | - | - |
| Distal | Trapezium | scaphoid | trapezoid | #1 and #2 |
| Distal | Trapezoid | scaphoid | trapezium, capitate | #2 |
| Distal | Capitate | scaphoid, lunate | trapezoid, hamate | #2, #3 and #4 |
| Distal | Hamate | triquetral, lunate | capitate | #4 and #5 |
Common characteristics of the carpal bones: Almost each bone (excepting the pisiform) presents six (6) surfaces.
Of these the palmar or anterior and the dorsal or posterior surfaces are rough, for ligamentous attachment; the dorsal surfaces being the broader, except in the lunate.
The superior or proximal, and inferior or distal surfaces are articular, the superior generally convex, the inferior concave; the medial and lateral surfaces are also articular where they are in contact with contiguous bones, otherwise they are rough and tuberculated.
The structure in all is similar: cancellous tissue enclosed in a layer of compact bone.
See also
Additional images
References
External links
- SUNY Labs 08:os-0101 - "Palm of the Hand: Carpal bones"
- Hand kinesiology at UK bone/wrist.html
|
|||||||||||||||||