Cardiomyopathy
| Cardiomyopathy Classification and external resources |
|
 |
|
|---|---|
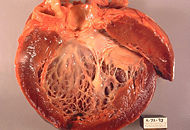
| Opened left ventricle of heart shows a thickened, dilated left ventricle with subendocardial fibrosis manifested as increased whiteness of endocardium. Autopsy. | |
| ICD-10 | I42.0 |
| ICD-9 | 425.4 |
| DiseasesDB | 2137 |
| MeSH | D009202 |
Cardiomyopathy, which literally means "heart muscle disease," is the deterioration of the function of the myocardium (i.e., the actual heart muscle) for any reason. People with cardiomyopathy are often at risk of arrhythmia or sudden cardiac death or both.[1]
Cardiomyopathies can generally be categorized into two groups, based on World Health Organization guidelines: extrinsic cardiomyopathies and intrinsic cardiomyopathies.[2]
Contents |
Extrinsic cardiomyopathies
These are cardiomyopathies where the primary pathology is outside the myocardium itself. Most cardiomyopathies are extrinsic, because by far the most common cause of a cardiomyopathy is ischemia. The World Health Organization calls these specific cardiomyopathies:[2]
- Coronary artery disease
- Congenital heart disease
- Nutritional diseases
- Ischemic (or ischaemic) cardiomyopathy
- Hypertensive cardiomyopathy
- Valvular cardiomyopathy
- Inflammatory cardiomyopathy
- Cardiomyopathy secondary to a systemic metabolic disease
- Alcoholic cardiomyopathy
- Diabetic cardiomyopathy
Ischemic cardiomyopathy
Ischemic cardiomyopathy is a weakness in the muscle of the heart due to inadequate oxygen delivery to the myocardium with coronary artery disease being the most common cause. Anemia and sleep apnea are relatively common conditions that can contribute to ischemic myocardium and hyperthyroidism can cause a 'relative' ischemia secondary to high output heart failure. Individuals with ischemic cardiomyopathy typically have a history of myocardial infarction (heart attack), although longstanding ischemia can cause enough damage to the myocardium to precipitate a clinically significant cardiomyopathy even in the absence of myocardial infarction. In a typical presentation, the area of the heart affected by a myocardial infarction will initially become necrotic as it dies, and will then be replaced by scar tissue (fibrosis). This fibrotic tissue is akinetic; it is no longer muscle and cannot contribute to the heart's function as a pump. If the akinetic region of the heart is substantial enough, the affected side of the heart (i.e. the left or right side) will go into failure, and this failure is the functional result of an ischemic cardiomyopathy.
Cardiomyopathy due to systemic diseases
Many diseases can result in cardiomyopathy. These include diseases like hemochromatosis, (an abnormal accumulation of iron in the liver and other organs), amyloidosis (an abnormal accumulation of the amyloid protein), diabetes, hyperthyroidism, lysosomal storage diseases and the muscular dystrophies.
Intrinsic cardiomyopathies
An intrinsic cardiomyopathy is weakness in the muscle of the heart that is not due to an identifiable external cause. To make a diagnosis of an intrinsic cardiomyopathy, significant coronary artery disease should be ruled out (amongst other things). The term intrinsic cardiomyopathy does not describe the specific etiology of weakened heart muscle. The intrinsic cardiomyopathies are a mixed-bag of disease states, each with their own causes.
Intrinsic cardiomyopathy has a number of causes including drug and alcohol toxicity, certain infections (including Hepatitis C), and various genetic and idiopathic (i.e., unknown) causes.
Intrinsic cardiomyopathies are generally classified into four types,[2][3] but additional types are also recognized:
- Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), the most common form, and one of the leading indications for heart transplantation. In DCM the heart (especially the left ventricle) is enlarged and the pumping function is diminished. Approximately 40% of cases are familial, but the genetics are poorly understood compared with HCM. In some cases it manifests as peripartum cardiomyopathy, and in other cases it may be associated with alcoholism.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM or HOCM), a genetic disorder caused by various mutations in genes encoding sarcomeric proteins. In HCM the heart muscle is thickened, which can obstruct blood flow and prevent the heart from functioning properly.
- Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) arises from an electrical disturbance of the heart in which heart muscle is replaced by fibrous scar tissue. The right ventricle is generally most affected.
- Restrictive cardiomyopathy (RCM) is an uncommon cardiomyopathy. The walls of the ventricles are stiff, but may not be thickened, and resist the normal filling of the heart with blood. A rare form of restrictive cardiomyopathy is the obliterative cardiomyopathy, seen in the hypereosinophilic syndrome. In this type of cardiomyopathy, the myocardium in the apices of the left and right ventricles becomes thickened and fibrotic, causing a decrease in the volumes of the ventricles and a type of restrictive cardiomyopathy.
- Noncompaction cardiomyopathy has been recognized as a separate type since the 1980s. The term refers to a cardiomyopathy where the left ventricle wall has failed to grow properly from birth and has a spongy appearance when viewed during an echocardiogram.
Signs and symptoms Cardiomyopathy is usually found incidentally - "case finding" - by healthcare professionals during a routine checkup. The only test for hypertension is a blood pressure measurement. Hypertension in isolation usually produces no symptoms although some people report headaches, fatigue, wanting to sleep more than usual, dizziness, blurred vision, facial flushing or tinnitus. [10]
Malignant Cardiomyopathy (or accelerated Cardiomyopathy) is distinct as a late phase in the condition, and may present with headaches, blurred vision and end-organ damage.
Cardiomyopathy is often confused with mental tension, stress and anxiety. While chronic anxiety and/or irritability is associated with poor outcomes in people with hypertension, it alone does not cause it. Accelerated hypertension is associated with somnolence, confusion, visual disturbances, and nausea and vomiting (hypertensive encephalopathy)
Treatment
Treatment depends on the type of cardiomyopathy, but may include medication, implanted pacemakers, defibrillators, or ventricular assist devices (LVADs), or ablation. The goal of treatment is often symptom relief, and some patients may eventually require a heart transplant. Treatment of cardiomyopathy (and other heart diseases) using alternative methods such as stem cell therapy is commercially available but is not supported by convincing evidence.
Famous cases
Dave Williams (musician) of Drowning Pool died of this disease in 2002.
Dr. Robert Atkins, inventor of "The Atkins Diet" suffered from this disease in the years before his death from a fall.
Alexei Cherepanov, 19 year old professional ice hockey player, died of this during an ice hockey game in 2008.
Michael James Hegstrand aka Road Warrior Hawk an American professional wrestler.
Slash, guitarist for Velvet Revolver, survived this disease.
Reggie Lewis, captain and all-star of the Boston Celtics, died from either Hypertrophic or Cocaine Cardiomyopathy at age 27.
Genetic causes of cardiomyopathy
| Phenotype | Inheritance pattern | Chromosomal locus | Gene | Protein | Skeletal myopathy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dilated cardiomyopathy | X-linked | Xp21 | dystrophin | Dystrophin | Duchenne / Becker muscular dystrophy |
| X-linked | Xq28 | G4.5 | Tafazzin | Barth syndrome | |
| Autosomal dominant | 15q14 | actin | Actin | Nemaline myopathy | |
| 2q35 | desmin | Desmin | Desmin myopathy | ||
| 5q33 | δ-sarcoglycan | δ-sarcoglycan | Limb girdle muscular dystrophy 2F | ||
| 1q32 | Troponin T | Troponin T | |||
| 14q11 | β-myosin heavy chain | β-myosin heavy chain | |||
| 15q2 | α-tropomyosin | α-tropomyosin | Nemaline myopathy | ||
| Midna | Mitochondrial respiratory chain | Mitochondrial respiratory chain | Mitochondrial myopathy | ||
| Dilated cardiomyopathy with conduction disease | Autosomal dominant | 1q21 | lamin A/C | Lamin A/C | Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy |
| Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy | Autosomal dominant | 14q11 | β-myosin heavy chain | β-myosin heavy chain | |
| 14q11 | β-myosin heavy chain | β-myosin heavey chain | |||
| 1q32 | Troponin T | Troponin T | |||
| 12q23 | Troponin T | Troponin T | |||
| 15q2 | α-tropomyosin | α-tropomyosin | Nemaline myopathy | ||
| 11q11 | myosin-binding protein C | myosin-binding protein C | |||
| 3p21 | myosin essential light chain | myosin essential light chain | |||
| 3p21 | myosin regulatory light chain | myosin regulatory light chain | |||
| 2p31 | titin | Titin | |||
| Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome | 7q3 | AMPK | AMPK | ||
| MIDINA | Mitochondrial respiratory chain | Mitochondrial respiratory chain | Mitochondrial myopathy | ||
| Left ventricular noncompaction | X-linked | Xq28 | G4.5 | Tafazzin | Barth syndrome |
| Autosomal dominant | 18q12 | α-dystrobrevin | α-Dystrobrevin | Muscular dystrophy |
Table from article *"The Failing Heart". Nature. Retrieved on June 15, 2007.
References
- ↑ Kasper, Denis L. et al (2005). Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 16th edn. McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-139140-1.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Richardson, P. et al (1996). "Report of the 1995 World Health Organization/International Society and Federation of Cardiology Task Force on the Definition and Classification of cardiomyopathies". Circulation 93 (5): 841–2. PMID 8598070. (Full text)
- ↑ Cardiomyopathy Association. "About cardiomyopathy". Retrieved on 2006-09-28.
External links
- [1] The Children's Cardiomyopathy Foundation is a non-profit that provides support to parents of affected children and accelerates research related to diagnosis, treatments and cures for all types of cardiomyopathies in children.
- The Cardiomyopathy Association A site is designed to provide you with information on the main forms of the heart muscle disease known as cardiomyopathy. Great information for adults and young.
- Cardiomyopathy information from Seattle Children's Hospital Heart Center
- Information from the Stanford Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Center
- Cardiomyopathy-related antibodies
- Treatment Cardiomyopathy (Alternative Medicine)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||