Carbonate

In chemistry, a carbonate is a salt or ester of carbonic acid.
Contents |
Applications
To test for the presence of the carbonate anion in a salt, the addition of dilute mineral acid (e.g. hydrochloric acid) will yield carbon dioxide gas.
Carbonate-containing salts are industrially and mineralogically ubiquitous. The term "carbonate" is also commonly used to refer to one of these salts or carbonate minerals. Most common is calcite, or calcium carbonate, CaCO3, the chief constituent of limestone. The process of removing carbon dioxide from these salts by heating is called calcination.
The term is also used as a verb, to describe the process of raising carbonate and bicarbonate concentrations in soda, see also carbonated water, either by the introduction under pressure of carbon dioxide gas into the bottle, or by dissolving carbonate or bicarbonate salts into the water.
Structure and bonding
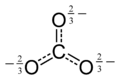
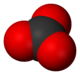
The carbonate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula CO32− and a molecular mass of 60.01 daltons; it consists of one central carbon atom surrounded by three identical oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement, and has D3h molecular symmetry. The carbonate ion carries a negative two formal charge and is the conjugate base of the hydrogen carbonate ion, HCO3−, which is the conjugate base of H2CO3, carbonic acid.
The structure and bonding of the carbonate ion cannot be properly represented by its Lewis structure, which depicts CO32− with two long single bonds and one short double bond:
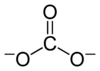
Resonance structures can be used to depict the carbonate ion:

In reality, CO32− has three equally long C-O bonds:
Chemical properties
A carbonate salt forms when a positively charged ion attaches to the negatively charged oxygen atoms of the ion, forming an ionic compound:
- 2M+ + CO32− → M2CO3
- M2+ + CO32− → MCO3
- 2M3+ + 3CO32− → M2(CO3)3
Most carbonate salts are insoluble in water at standard temperature and pressure, with solubility constants of less than 1×10−8. Exceptions include sodium, potassium and ammonium carbonates.
In aqueous solution, carbonate, bicarbonate, carbon dioxide, and carbonic acid exist together in a dynamic equilibrium. In strongly basic conditions, the carbonate ion predominates, while in weakly basic conditions, the bicarbonate ion is prevalent. In more acid conditions, aqueous carbon dioxide, CO2(aq), is the main form, which, with water, H2O, is in equilibrium with carbonic acid - the equilibrium lies strongly towards carbon dioxide. Thus sodium carbonate is basic, sodium bicarbonate is weakly basic, while carbon dioxide itself is a weak acid.
Carbonated water is formed by dissolving CO2 in water under pressure. When the partial pressure of CO2 is reduced, for example when a can of soda is opened, the equilibrium for each of the forms of carbonate (carbonate, bicarbonate, carbon dioxide, and carbonic acid) shifts until the concentration of CO2 in the solution is equal to the solubility of CO2 at that temperature and pressure. In living systems an enzyme, carbonic anhydrase, speeds the interconversion of CO2 and carbonic acid.
Acid-base chemistry
The carbonate ion (CO32−) is a moderately strong base. It is a conjugate base of the weakly acidic bicarbonate (IUPAC name hydrogen carbonate HCO3−), itself a moderately strong conjugate base of the still weakly acidic carbonic acid. As such in aqueous solution, the carbonate ion seeks to reclaim hydrogen atoms.
Organic carbonates
In organic chemistry a carbonate can also refer to a functional group within a larger molecule that contains a carbon atom bound to three oxygen atoms, one which is double bonded. These compounds are also known as organocarbonates or carbonate esters, and have the general formula ROCOOR′, or RR′CO3. Important organocarbonates include dimethyl carbonate, the cyclic compounds ethylene carbonate and propylene carbonate, and the toxic triphosgene.
Biological Significance
It works as a buffer in the blood as follows: when pH is too low, the concentration of hydrogen ions is too high, so you exhale CO2. This will cause the equation to shift left, essentially decreasing the concentration of H+ ions, causing a more basic pH.
When pH is too high, the concentration of hydrogen ions in the blood is too low, so the kidneys excrete bicarbonate (HCO3−). This causes the equation to shift right, essentially increasing the concentration of hydrogen ions, causing a more acidic pH.
Carbonate salts
- See also: Category:Carbonates
- Carbonate overview:
| H2CO3 | He | |||||||||||||||||
| Li2CO3 | BeCO3 | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | |||||||||||
| Na2CO3 | MgCO3 | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | |||||||||||
| K2CO3 | CaCO3 | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | MnCO3 | FeCO3 | CoCO3 | NiCO3 | CuCO3 | ZnCO3 | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr | |
| Rb2CO3 | SrCO3 | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag2CO3 | CdCO3 | In | Sn | Sb | Te | CI | Xe | |
| Cs2CO3 | BaCO3 | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl2CO3 | PbCO3 | Bi | Po | At | Rn | ||
| Fr | Ra | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Uub | Uut | Uuq | Uup | Uuh | Uus | Uuo | ||
| ↓ | ||||||||||||||||||
| La2(CO3)3 | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ||||
| Ac | Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | ||||
History
It is generally thought that the presence of carbonates in rock is unchallengable evidence for the presence of liquid water. Recent observations of the Planetary nebula NGC 6302 shows evidence for carbonates in space[1], where aqueous alteration similar to that on Earth is unlikely. Other minerals have been proposed which would fit the observations.
Significant carbonate deposits have not been found on Mars via remote sensing or in situ missions, even though Martian meteorites contain small amounts. Groundwater may have existed at both Gusev[2] and Meridiani Planum[3].
References
- ↑ Kemper, F., Molster, F.J., Jager, C. and Waters, L.B.F.M. (2002) The mineral composition and spatial distribution of the dust ejecta of NGC 6302. Astronomy & Astrophysics 394, 679-690.
- ↑ Squyres et al., (2007) doi 10.1126/science.1139045
- ↑ Squyres et al., (2006) doi 10.1029/2006JE002771
|
|||||||||||
See also
Bicarbonate