Canadian dollar
| Canadian dollar dollar canadien (French) |
|||||
|
|||||
| ISO 4217 Code | CAD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| User(s) | |||||
| Inflation | 2.4% | ||||
| Source | The World Factbook, 2007 est. | ||||
| Subunit | |||||
| 1/100 | cent (English) and (French) | ||||
| Symbol | $ or C$ | ||||
| cent (English) and (French) | ¢ | ||||
| Nickname | loonie, buck (English) huard, piastre (pronounced piasse in popular usage) (French) |
||||
| Coins | |||||
| Freq. used | 1¢, 5¢, 10¢, 25¢, $1, $2 | ||||
| Rarely used | 50¢ | ||||
| Banknotes | |||||
| Freq. used | $5, $10, $20, $50, $100 | ||||
| Central bank | Bank of Canada | ||||
| Website | www.bankofcanada.ca | ||||
| Printer | Canadian Bank Note Company, BA International Inc. | ||||
| Mint | Royal Canadian Mint | ||||
| Website | www.mint.ca | ||||
The Canadian dollar (sign: $; code: CAD) is the currency of Canada. It is normally abbreviated with the dollar sign $, or C$ to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies.[1] It is divided into 100 cents. As of 2007, the Canadian dollar was the 7th most traded currency in the world.[2]
Contents |
History
Gold dollar
In 1841, the new Province of Canada declared that its dollar was equal to one-tenth the gold Eagle coin which was 10 U.S. dollar and was worth 5 s. (5 shillings) in local currency. The silver Spanish dollars were rated at 5 s. 1 d. and the British sovereign was rated at £1 4 s. 4 d. , the proper value due to its gold content compared to that of the gold U.S. dollar.
Independent Canadian dollar
The Province of Canada declared that all accounts would be kept in dollars and cents as of January 1, 1858, and ordered the issue of the first official Canadian coins in the same year. The dollar was pegged at par with the U.S. dollar, on a gold standard of $1 = 23.22 grains (1.505 g) of gold.
The colonies that came together in the Canadian Confederation progressively adopted a decimal system over the next few years. New Brunswick, British Columbia and Prince Edward Island adopted dollars equivalent to the Canadian dollar (see New Brunswick dollar, British Columbia dollar and Prince Edward Island dollar). However, Nova Scotia and Newfoundland did not adopt the same dollar (see Nova Scotian dollar and Newfoundland dollar). Nova Scotia retained its own currency until 1871, but Newfoundland issued its own currency until joining Confederation in 1949, although the value of the Newfoundland dollar was adjusted in 1895 to make it equal to the Canadian dollar.
| Currencies used in Canada | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Currency | Dates in use | Value in British pounds | Value in Canadian dollars |
| Canadian pound | 1841–1858 | 16s 5.3d | $4 |
| Canadian dollar | 1858– | 4s 1.3d | $1 |
| New Brunswick dollar | 1860–1867 | ||
| British Columbia dollar | 1865–1871 | ||
| Prince Edward Island dollar | 1871–1873 | ||
| Nova Scotian dollar | 1860–1871 | 4s | $0.973 |
| Newfoundland dollar | 1865-1895 | 4s 2d | $1.014 |
| 1895–1949 | 4s 1.3d | $1 | |
The federal Parliament passed the Uniform Currency Act in April 1871,[3] tying up loose ends as to the currencies of the various provinces and replacing them with a common Canadian dollar. The gold standard was temporarily abandoned during the First World War and definitively abolished on April 10, 1933. At the outbreak of the Second World War, the exchange rate to the U.S. dollar was fixed at 1.1 Canadian dollars = 1 U.S. dollar. This was changed to parity in 1946. In 1949, sterling was devalued and Canada followed, returning to a peg of 1.1 Canadian dollars = 1 U.S. dollar. However, Canada allowed its dollar to float in 1950, only returning to a fixed exchange rate in 1962, when the dollar was pegged at 1 Canadian dollar = 0.925 U.S. dollar. This peg lasted until 1970, after which the currency's value has floated.
Terminology
Canadian English, like American English, uses the slang term "buck" for a dollar. Because of the appearance of the common loon on the back of the dollar coin that replaced the dollar bill in 1987, the word "loonie" was adopted in Canadian parlance to distinguish the Canadian dollar from other currencies, as in "The loonie performed well today on currency markets." When the two-dollar coin was introduced in 1996, the derivative word "toonie" became the common word for it in Canadian English slang.
In French, the currency is also called le dollar; Canadian French slang terms include piastre or piasse (same as "buck", but the original word used in eighteenth-century French to translate "dollar") and huard (equivalent to "loonie", since huard is French for "loon," the bird appearing on the coin). The French pronunciation of "cent" (pronounced similarly to English as /sɛnt/, not like the word for hundred /sɛ̃/)[4] is generally used for the subdivision; sou is another, informal, term.
Coins
In 1858, bronze 1¢ and .925 silver 5¢, 10¢ and 20¢ coins were issued by the Province of Canada. Except for 1¢ coins struck in 1859, no more coins were issued until 1870, when production of the 5¢ and 10¢ was resumed and silver 25¢ and 50¢ were introduced. Between 1908 and 1919, sovereigns (legal tender in Canada for $4.866) were struck in Ottawa with a "C" mintmark. Gold $5 and $10 coins were issued between 1912 and 1914.
In 1920, the size of the 1¢ was reduced and the silver fineness was reduced to .800. In 1922, the silver 5¢ was replaced by a larger, nickel coin. In 1935, a silver $1 coin was introduced. In 1942, as a war-time measure, nickel was replaced by tombac in the 5¢ coin, which was changed from round to dodecagonal. Chromium-plated steel was used for the 5¢ between 1944 and 1945 and between 1951 and 1954, before nickel was permanently readopted. The 5¢ returned to a round shape in 1963.
In 1968, .500 silver 10¢ and 25¢ coins were issued, before silver was replaced by nickel. At the same time, the sizes of the 50¢ and $1 coins were reduced. In 1982, the 1¢ coin was changed to dodecagonal and the 5¢ was switched to a cupro-nickel alloy. In 1987, a $1 coin struck in aureate-plated nickel was introduced. A bimetallic $2 coin followed in 1996. In 1997, copper-plated zinc replaced bronze in the 1¢. This was followed, in 2000, by the introduction of plated-steel 1¢, 5¢, 10¢, 25¢ and 50¢ coins, with the 1¢ plated in copper and the others plated in cupro-nickel.
Coins are produced by the Royal Canadian Mint in Winnipeg, Manitoba, and currently issued in denominations of 1¢ (penny), 5¢ (nickel), 10¢ (dime), 25¢ (quarter), 50¢ (50¢ piece) (though the 50¢ piece is rarely used), $1 (loonie), and $2 (toonie). The standard set of designs has Canadian symbols, usually wildlife, on the reverse, and an effigy of Elizabeth II on the obverse. However, some pennies, nickels, and dimes remain in circulation that bear the effigy of George VI. Commemorative coins with differing reverses are also issued on an irregular basis. 50¢ coins are rarely found in circulation; they are often collected and not regularly used in day-to-day transactions. There have been repeated talks about removing the penny from circulation as it is estimated that it costs the Royal Canadian Mint up to four cents to produce and distribute a one-cent coin.[5] The Canadian penny costs at least C$130 million annually to keep in circulation, estimates a financial institution that called for an end to the penny.[6] A 2007 survey shows that only 37% of Canadians use pennies but the government continues to produce about 816 million pennies per year, equal to 25 pennies per Canadian.[6]
Banknotes

The first paper money issued in Canada denominated in dollars were British Army Bills, issued between 1813 and 1815 in denominations between $1 and $400. These were emergency issues due to the War of 1812. The first banknotes were issued in 1817 by the Montreal Bank. Large numbers of chartered banks were founded in the 1830s, 1850s, 1860s and 1870s, although many issued paper money for only a short time. Others, including the Montreal Bank (later called the Bank of Montreal), issued notes for several decades. Until 1858, many notes were issued denominated in both shillings/pounds and dollars (5 shillings = $1). A large number of different denominations were issued, including $1, $2, $3, $4, $5, $10, $20, $25, $40, $50, $100, $500 and $1000. After 1858, only dollar denominations were used. See Canadian chartered bank notes for more information.
After its establishment in 1841, the Province of Canada began issuing paper money. Notes were produced for the government by the Bank of Montreal between 1842 and 1862, in denominations of $4, $5, $10, $20, $50 and $100. In 1866, the Province of Canada began issuing its own paper money, in denominations of $1, $2, $5, $10, $20, $50, $100 and $500. In 1870, following Confederation, the Dominion of Canada introduced 25¢ notes along with new issues of $1, $2, $500 and $1000. $50 and $100 notes followed in 1872 but the bulk of later government note production was of $1 and $2 note, with $4 added in 1882. Denominations of $500, $1000, $5000 and $50,000 were issued after 1896 for bank transactions only.
The Bank Act of 1871 limited the smallest denomination the chartered banks could issue to $4, increased to $5 in 1880. To facilitate purchases below $5 without using Dominion notes, Molsons Bank issued $6 and $7 notes in 1871. The government issued $5 notes from 1912. The last 25¢ notes, known as shinplasters due to their small size, were dated 1923.
In 1935, with only ten chartered banks still issuing notes, the Bank of Canada was founded and began issuing notes in denominations of $1, $2, $5, $10, $20, $50, $100, $500 and $1000. In 1944, the chartered banks were prohibited from issuing their own currency, with the Royal Bank of Canada and the Bank of Montreal among the last to issue notes.
Although the $1 coin was introduced in 1935, it was not until the introduction of the "loonie" that the banknote was withdrawn from circulation. The $2 note was also replaced by a coin in 1996. All banknotes are currently printed by the Canadian Bank Note Company and BA International Inc on behalf of the Bank of Canada.
In 2000, the Bank of Canada stopped issuing $1000 notes and began to withdraw them from circulation, "as part of the fight against money laundering and organized crime."[7]
Even when banknotes are withdrawn, they remain legal tender and can be used or traded at banks. However, once received by the bank, they must be forwarded to the Central Bank for destruction.
Legal tender
Canadian dollar banknotes issued by the Bank of Canada are legal tender in Canada. However, commercial transactions may legally be settled in any manner agreed by the parties involved.
Legal tender of Canadian coinage is governed by the Currency Act which sets out limits of:[8]
- $40 if the denomination is $2 or greater but does not exceed $10;
- $25 if the denomination is $1;
- $10 if the denomination is 10¢ or greater but less than $1;
- $5 if the denomination is 5¢;
- 25¢ if the denomination is 1¢.
Retailers in Canada may refuse bank notes without breaking the law. According to legal guidelines, the method of payment has to be mutually agreed upon by the parties involved with the transactions. For example, convenience stores may refuse $100 bank notes if they feel that would put them at risk of being counterfeit victims; however, official policy suggests that the retailers should evaluate the impact of that approach. In the case that no mutually acceptable form of payment can be found for the tender, the parties involved should seek legal advice.[9]
Canadian Dollars are accepted by some businesses in the northernmost cities of United States, just as American Dollars are accepted by many Canadian businesses in cities close to the border.
Value
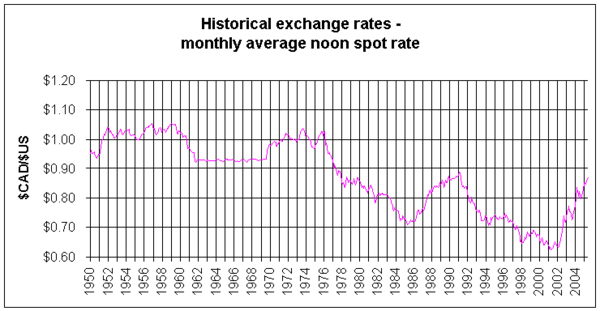
Unlike other currencies in the Bretton Woods system, whose values were fixed, the Canadian dollar was allowed to float from 1950 to 1962. Between 1952 to 1960, the Canadian dollar traded at a slight premium over the U.S. dollar, reaching a high of US$1.0614 on August 20, 1957.
The Canadian dollar fell considerably after 1960, and this contributed to Prime Minister John Diefenbaker's defeat in the 1963 election. The Canadian dollar returned to a fixed exchange rate regime in 1962 when its value was set at US$0.925, where it remained until 1970.
As an inflation-fighting measure, the Canadian dollar was allowed to float in 1970. Its value appreciated and it was worth more than the U.S. dollar for part of the 1970s. The high point was on April 25, 1974, when it reached US$1.0443.

The Canadian dollar fell in value against its American counterpart during the technological boom of the 1990s that was centred on the United States, and was traded for as little as 61.79¢ U.S. on 21 January 2002, which was an all-time low. [10] Since then, its value against all major currencies has risen due, in part, to high prices for commodities (especially oil) that Canada exports.
The CAD's value against the U.S. dollar rose sharply in 2007 due to the continued strength of the Canadian economy and the U.S. currency's weakness on world markets. During trading on September 20, 2007 it met the U.S. greenback at parity for the first time since November 25, 1976.[11]
Inflation in the value of the Canadian dollar was fairly low since the 1990s, but had been severe for some decades before that. In 2007 the Canadian dollar rebounded remarkably, soaring 23% in value.
On September 28, 2007, the Canadian dollar closed above the U.S. dollar for the first time in 30 years, at US$1.0052. [12] On November 7, 2007, it hit US$1.1024 during trading, a modern-day high[13] after China announced it would diversify its US$1.43 trillion foreign exchange reserve away from the U.S. dollar. By November 30, however, the Canadian dollar was once again at par with the U.S. dollar, and on December 4, the dollar had retreated back to US$0.98, through a cut in interest rates by the Bank of Canada, due to concerns about exports to the U.S. The rate has since been fluctuating between US$0.9644 and US$1.0298,[14] after starting 2008 at just under US$1.01. (The dollar has been as high as US$2.78, reached on 11 July 1864 after the United States had temporarily abandoned the gold standard.) Since late July 2008, however, the Canadian dollar has dropped considerably, reaching 84 U.S. cents by October 17 and dropping to 80 cents by October 22.[15]
Since 84.2% of Canada's exports go to the U.S., and 56.7% of imports into Canada come from the U.S.,[16] Canadians are mainly interested in the value of their currency against the U.S. dollar. Although domestic concerns arise when the dollar trades much lower than its U.S. counterpart, there is also concern among exporters when the dollar appreciates quickly. The rapid rise in the value of the dollar increases the price of Canadian exports to the U.S. On the other hand, there are advantages to a rising dollar, in that it is cheaper for Canadian industries to purchase foreign material and businesses.
The Bank of Canada has no specific target value for the Canadian dollar and has not intervened in foreign exchange markets since 1998.[17] The Bank's current position is that market conditions should determine the worth of the Canadian dollar.
On world markets, the Canadian dollar historically tended to move in tandem with the U.S. dollar. At times an apparently rising Canadian dollar (against the U.S. dollar) may be decreasing against other international currencies; however, during the rise of the Canadian dollar since 2002, it has gained value against the U.S. dollar as well as other international currencies.
Due to its soaring value and new record highs, the Canadian dollar was named the Canadian Newsmaker of the Year for 2007 by Time magazine.[18]
Reserve currency
A number of central banks keep Canadian dollars as a reserve currency. The Canadian dollar is considered to be a benchmark currency.[19]
In the economy of the Americas as a whole the dollar plays a similar role to the Australian Dollar (AUD) does in the Asia-Pacific region. The dollar (as a regional reserve currency) has been an important part of the British, French and Dutch Caribbean state's economies since the 1950s.
By observing how the Canadian dollar behaves against the U.S. dollar, global economists can indirectly observe internal behaviors and patterns in the US economy. The dollar has only evolved as a reserve currency since the 1970s when it was floated against all other world currencies.
| From Yahoo! Finance: | AUD CHF EUR GBP HKD JPY USD |
| From XE.com: | AUD CHF EUR GBP HKD JPY USD |
| From OANDA.com: | AUD CHF EUR GBP HKD JPY USD |
See also
References
- ↑ There are various common abbreviations to distinguish the Canadian dollar from others: while the ISO currency code CAD (a three-character code without monetary symbols) is common, no single system is universally accepted. C$ is recommended by the Canadian government (e.g., per The Canadian Style guide) and is used by the International Monetary Fund, while Editing Canadian English indicates Can$ and CDN$; both guides note the ISO scheme/code. The abbreviation CA$ is also used, e.g., in some software packages.
- ↑ http://www.bis.org/publ/rpfxf07t.pdf (December 2007) Bank for International Settlements
- ↑ "1871 – Uniform Currency Act". Canadian Economy Online, Government of Canada. Retrieved on 2008-02-18.
- ↑ Guilloton, Noëlle; Cajolet-Laganière, Hélène (2005). Le français au bureau. Les publications du Québec. pp. p. 467. ISBN 2-551-19684-1.
- ↑ Chande, Dinu; Fisher, Timothy. "Have a Penny? Need a Penny?" (.PDF) (in French/English). economics.ca. Retrieved on 2007-02-26.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Agence France Presse (2007-02-15). "Financial group lobbies for 'penny-less' Canadian economy", Yahoo! Canada News. Retrieved on 2007-02-26.
- ↑ "Bank of Canada to Stop Issuing $1000 Note" (.HTML). Bank of Canada. Retrieved on 2007-12-14.
- ↑ "Currency Act ( R.S., 1985, c. C-52 )". Canada Department of Justice. Retrieved on 2008-02-17.
- ↑ "Currency Counterfeiting – FAQ". Royal Canadian Mounted Police. Retrieved on 2008-02-17.
- ↑ oanda.com. "Historical exchange rate of CAD to USD from December 21, 2001 to February 21, 2002". Retrieved on 2007-03-14.
- ↑ "Topsy-turvy world last time loonie was on par with greenback", Canadian Press (2007-09-20). Retrieved on 2007-09-21.
- ↑ "Loonie closes above parity with greenback" (.html), ctv.ca. Retrieved on 2007-09-28.
- ↑ , Tavia Grant (2007-11-07). "China sends loonie flying above $1.10" (.html), The Globe and Mail. Retrieved on 2007-11-07.
- ↑ Big price gap still exists between Canadian, U.S. goods: study
- ↑ [1]
- ↑ Central Intelligence Agency. "The World Factbook – Canada". Retrieved on 2007-02-15.
- ↑ Bank of Canada policy on dollar valuation and intervention in FOREX markets
- ↑ Lofty loonie named Time's top Canadian newsmaker
- ↑ Benchmark currencies of the world
- Krause, Chester L. and Clifford Mishler (1991). Standard Catalog of World Coins: 1801-1991 (18th ed. ed.). Krause Publications. ISBN 0873411501.
- Pick, Albert (1994). Standard Catalog of World Paper Money: General Issues. Colin R. Bruce II and Neil Shafer (editors) (7th ed. ed.). Krause Publications. ISBN 0-87341-207-9.
- Pick, Albert (1990). Standard Catalog of World Paper Money: Specialized Issues. Colin R. Bruce II and Neil Shafer (editors) (6th ed. ed.). Krause Publications. ISBN 0-87341-149-8.
External links
- Exchange Rate Lookup
- A History of the Canadian dollar
- Bank of Canada — bank notes
- Royal Canadian Mint
- History of the earliest forms currency in Canada
- Canadian Paper Money A resource for those interested in learning about and collecting Canadian paper currency
- Banknotes of Canada at Will's Online World Paper Money Gallery
- Maple Leaf Web: The Canadian Dollar: Nature and Impacts of Canadian Exchange Rates
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||