Anatolia

Anatolia (Turkish: Anadolu, Greek: Ανατολία, Anatolía) or Asia Minor is a region of Western Asia, comprising most of the modern Republic of Turkey. It is a geographic region bounded by the Black Sea to the north, the Caucasus to the northeast, the Aegean Sea to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, Greater Syria (Upper Mesopotamia) to the southeast and Transcaucasia and the Iranian plateau to the east.
Contents |
Name
-
For more details on this topic, see Names of Anatolia.
The name Anatolia comes from the Greek Aνατολή (Αnatolí), "rise (i.e. sunrise)", or Ανατολία (Anatolía), "(land) of the sunrise" or simply the "East".[1] It likely dates back at least 3,000 years, from the Ionian settlement period in the 1st millennium BC. (See also Ionian League). The Byzantine Greek term Anatolicon ("Eastern") signified the lands to the east of Europe and of the Roman Empire's late-era capital city of Constantinople, also New Rome (now Istanbul).[2] The etymology of the word supports the idea that Anatolia was a peninsula bordered by the Black Sea, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Eastern Taurus Range.
The Turkish form Anadolu derives from the Greek version—both which predated the growth of Constantinople across the Bosporus strait to both continental shores. Turkish folk etymology further breaks down the geographical term into two words: Ana ("mother") and Dolu ("full"). Thus, the name means "Full of Motherliness", and is used to advance a pedagogical ideal: women's contribution of mother's milk to national masculine bravery.[3] Less literally, the term is sometimes interpreted as Mother of Cities, referring to Constantinople, perhaps dating to the pre-Islamic era when the Byzantine Empire was the biggest international power known in that part of Asia, and occupied the entire region.
Physical geography
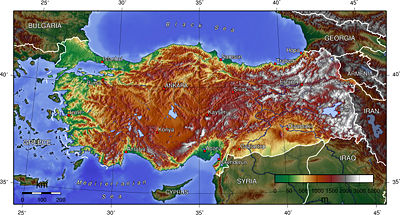
The Anatolian peninsula is bounded by the Black Sea to the north, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean Sea (itself an arm of the Mediterranean) to the west, and the bulk of the Asian mainland to the east.
Anatolia's terrain is structurally complex. A central massif composed of uplifted blocks and downfolded troughs, covered by recent deposits and giving the appearance of a plateau with rough terrain, is wedged between two folded mountain ranges that converge in the east. True lowland is confined to a few narrow coastal strips along the Black Sea and Mediterranean Sea coasts. Flat or gently sloping land is rare and largely confined to the deltas of the Kızıl River, the coastal plains of Çukurova, and the valley floors of the Gediz River and the Büyük Menderes River, and some interior high plains in Anatolia, mainly around Tuz Gölü (Salt Lake) and Konya Ovası (Konya Basin).
Black Sea region
The Black Sea region has a steep, rocky coast with rivers that cascade through the gorges of the coastal ranges. The North Anatolian mountains are an interrupted chain of folded highlands that generally parallel the Black Sea coast. A few larger rivers, those cutting back through the Pontic Mountains (Turkish: Kaçkar Dağları), have tributaries that flow in broad, elevated basins. Rivers flow from the mountains toward the Black Sea trough in lengthy valleys.
Access inland from the coast is limited to a few narrow valleys because mountain ridges, with elevations of 1,525 to 1,800 metres (5,000 to 5,900 ft) in the west and 3,000 to 4,000 metres (10,000 to 13,000 ft) in the east in Kaçkar Mountains, form an almost unbroken wall separating the coast from the interior. The higher slopes facing southwest tend to be densely wet. Because of these natural conditions, the Black Sea coast historically has been isolated from Anatolia. The southern slopes—facing the Anatolian Plateau—are mostly unwooded, but the northern slopes contain dense growths of both deciduous and evergreen trees.
Mediterranean region

The narrow coastal plains of the Mediterranean region, separated from the Anatolian plateau by the Taurus Mountains, which reach elevations of 2,000 to 2,750 metres (6,600 to 9,000 ft), are cultivated intensively. Fertile soils and a warm climate make the Mediterranean coast ideal for growing citrus fruits, grapes, figs, bananas, various vegetables, barley, wheat, and, in irrigated areas, rice and cotton. The Çukurova in the east is a plain that is the most developed agricultural area of the Mediterranean region. If considered the quantam physics appeared to have altered the apparent shape of the northeasternward end of the sea. There was a giant land slide estimated to have happened about 3,000 years ago. It wiped out several land bridges creating the black sea from the mediterranean. If it were not for this catastrophic event sea level may be a few inches higher, directly resulting in the disappearance of the entire Anatolia Peninsula due to the fact that it is, for the most part, within 100 feet of sea level.
Anatolian plateau
Stretching inland from the Aegean coastal plain, Central Anatolia occupies the area between the two zones of the folded mountains, extending east to the point where the two ranges converge. The plateau-like, semiarid highlands of Anatolia are considered the heartland of the country. The region varies in elevation from 600 to 1,200 meters (2,000 to 4,000 ft) from west to east. The two largest basins on the plateau are the Konya Ovası and the basin occupied by the large salt lake, Tuz Gölü. Both basins are characterized by inland drainage. Wooded areas are confined to the northwest and northeast of the plateau.
Mountains close to the coast prevent Mediterranean influences from extending inland, giving the interior of Turkey a continental climate with distinct seasons. The Anatolian Plateau is much more subject to extremes than are the coastal areas. Winters on the plateau are especially severe. Temperatures of -30 °C to -40 °C (-22 °F to -40 °F) can occur in the mountainous areas in the east, and snow may lie on the ground 120 days of the year. In the west, winter temperatures average below 1 °C (34 °F). Summers are hot and dry, with temperatures above 30 °C (86 °F). Annual precipitation averages about 400 mm (15.7 inches), with actual amounts determined by elevation. The driest regions are the Konya Ovası and the Malatya Ovası, where annual rainfall frequently is less than 300 mm (11.8 inches). May is generally the driest month and July and August are the wettest.
Eastern Anatolia
Eastern Anatolia where the Pontus and Taurus mountain ranges converge, is rugged country with higher elevations, a more severe climate, and greater precipitation than are found on the Anatolian Plateau. The region is known as the Anti-Taurus, and the average elevation of its peaks exceeds 3,000 m. Mount Ararat, at 5,137 metres (16,854 ft) the highest point in Turkey, is located in the Anti-Taurus. Lake Van is situated in the mountains at an elevation of 1,546 metres (5,072 ft). The headwaters of three major rivers arise in the Anti-Taurus: the east-flowing Aras River, which empties into the Caspian Sea; the south-flowing Euphrates and Tigris join in Iraq before emptying into the Persian Gulf. Several small streams that empty into the Black Sea or landlocked Lake Van also originate in these mountains.
Southeast Anatolia lies south of the Anti-Taurus Mountains. It is a region of rolling hills and a broad plateau surface that extends into Syria. Elevations decrease gradually, from about 800 metres (2,600 ft) in the north to about 500 metres (1,600 ft) in the south. Traditionally, wheat and barley were the main crops of the region, but the inauguration of major new irrigation projects in the 1980s has led to greater agricultural diversity and development.
Climate
Anatolia has a varied range of climates. This is partly due to the reason that Anatolia covers such a vast expanse of land. In fact, it goes all the way into southwestern Russia, where it is covered by temperate forests.
Ecoregions

Anatolia's diverse topography and climate has fostered a similar diversity of plant and animal communities.
The mountains and coastal plain of northern Anatolia, with its humid and mild climate, is home to temperate broadleaf, mixed, and coniferous forests. The central and eastern plateau, with its drier continental climate, is home to deciduous forests and forest steppes. Western and southern Anatolia, which have a Mediterranean climate, are home to Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and shrub ecoregions.
- Euxine-Colchic deciduous forests: These temperate broadleaf and mixed forests extend across northern Anatolia, lying between the mountains of northern Anatolia and the Black Sea. They include the enclaves of temperate rainforest lying along the southeastern coast of the Black Sea in eastern Turkey and Georgia.[4]
- Northern Anatolian conifer and deciduous forests: These forests occupy the mountains of northern Anatolia, running east and west between the coastal Euxine-Colchic forests and the drier, continental climate forests of central and eastern Anatolia. [5]
- Central Anatolian deciduous forests: These forests of deciduous oaks and evergreen pines cover the plateau of central Anatolia. [6]
- Central Anatolian steppe: These dry grasslands cover the drier valleys and surround the saline lakes of central Anatolia, and include halophytic (salt tolerant) plant communities. [7]
- Eastern Anatolian deciduous forests: This ecoregion occupies the plateau of eastern Anatolia. The drier and more continental climate is home to steppe-forests dominated by deciduous oaks, with areas of shrubland, montane forest, and valley forest. [8]
- Anatolian conifer and deciduous mixed forests: These forests occupy the western, Mediterranean-climate portion of the Anatolian plateau. Pine forests and mixed pine and oak woodlands and shrublands are predominant. [9]
- Aegean and Western Turkey sclerophyllous and mixed forests: These Mediterranean-climate forests occupy the coastal lowlands and valleys of western Anatolia bordering the Aegean Sea. The ecoregion is home to forests of Turkish Pine (Pinus brutia), oak forests and woodlands, and maquis shrubland of Turkish Pine and evergreen sclerophyllous trees and shrubs, including Olive (Olea europaea), Strawberry Tree (Arbutus unedo), Arbutus andrachne, Kermes Oak (Quercus coccifera), and Bay Laurel (Laurus nobilis). [10]
- Southern Anatolian montane conifer and deciduous forests: These mountain forests occupy the Mediterranean-climate Taurus Mountains of southern Anatolia. Conifer forests are predominant, chiefly Anatolian black pine (Pinus nigra), Cedar of Lebanon (Cedrus libani), Taurus fir (Abies cilicica), and juniper (Juniperus foetidissima and J. excelsa). Broadleaf trees include oaks, hornbeam, and maples. [11]
- Eastern Mediterranean conifer-sclerophyllous-broadleaf forests: This ecoregion occupies the coastal strip of southern Anatolia, between the Taurus Mountains and the Mediterranean Sea. Plant communities include broadleaf sclerophyllous maquis shrublands, forests of Aleppo Pine (Pinus halepensis) and Turkish Pine (Pinus brutia), and dry oak (Quercus spp.) woodlands and steppes. [12]
History
Eastern Anatolia contains the oldest monumental structures in the world. For example, the monumental structures at Göbekli Tepe were built by hunters and gatherers, a thousand years before the development of agriculture. Eastern Anatolia is also a hearth region for the Neolithic revolution, one of the earliest areas in which humans domesticated plants and animals. Neolithic sites such as Çatalhöyük, Çayönü, Nevali Cori, and Hacilar represent the world's oldest known agricultural villages.
The earliest historical records of Anatolia are from the Akkadian Empire under Sargon in the 24th century BC. The region was famous for exporting various raw materials.[13] The Assyrian Empire claimed the resources, notably silver. One of the numerous Assyrian cuneiform records found in Anatolia at Kanesh uses an advanced system of trading computations and credit lines.[13]
Unlike the Akkadians and the Assyrians, whose Anatolian possessions were peripheral to their core lands in Mesopotamia, the Hittites were centered at Hattusa in north-central Anatolia. Speakers of an Indo-European language, they established a kingdom in the 18th century BC, and built an empire which reached its height in the 14th century BC. The empire included a large part of Anatolia, north-western Syria, and upper Mesopotamia. After 1180 BC, the empire disintegrated into several independent "Neo-Hittite" city-states, some surviving until as late as the 8th century BC.
The Armenians in the 1st century BC established the Armenian kingdom under Tigran who reigned throughout much of the region situated between the Caspian, Black and Mediterranean seas. Asia Minor is known as the birthplace of coinage as a medium of exchange (some time in the 7th century BC), which flourished during the Greek and Roman eras.[14][15]
The Turkish language was introduced gradually with the conquest of Anatolia by Turkic peoples from the 11th century AD. Anatolia remained multi-ethnic until the early 20th century (see Rise of Nationalism under the Ottoman Empire). During World War I the Armenian Genocide almost eliminated the Armenian population of Anatolia. The entire Greek population was also eliminated in the post-WW1 period: some fled with the defeated Greek army (see Turkish War of Independence), but most were forced out during the 1922 population exchange between Greece and Turkey. As the Ottoman Empire fragmented during the Balkan Wars much of the non-Christian populations of its former possessions, mainly Balkan Muslims, flocked to Anatolia and were settled in various locations.[16].
Since the foundation of the Republic of Turkey in 1923, most of Anatolia has been part of Turkey, its inhabitants mainly Turks (a generic and very general term) and Kurds, among other minorities (see demographics of Turkey and history of Turkey).
References
- ↑ "Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, A Greek-English Lexicon".
- ↑ "On the First Thema, Called Anatolikon. This theme is called Anatolikon, not because it is above and in the direction of the east where the sun rises, but because it lies East of Byzantium and Europe." Constantine VII Porphyogenitus, De Thematibus, ed. A. Pertusi. Vatican: Biblioteca Apostolica Vaticana, 1952, pp. 59–61.
- ↑ Sam Kaplan, "Din-u Devlet All Over Again?", International Journal of Middle East Studies, 34:117 (2002).
- ↑ "Euxine-Colchic deciduous forests" WWF scientific report. Accessed May 25 2008. [1]
- ↑ "Northern Anatolian conifer and deciduous forests" WWF scientific report. Accessed May 25 2008. [2]
- ↑ "Central Anatolian deciduous forests" National Geographic ecoregion profile. Accessed May 25, 2008 [3]
- ↑ "Central Anatolian steppe" WWF scientific Report. Accessed May 25 2008 [4]
- ↑ "Eastern Anatolian deciduous forests" WWF scientific report. Accessed May 25 2008. [5]
- ↑ "Anatolian conifer and deciduous mixed forests" WWF scientific report. Accessed May 25 2008 [6]
- ↑ Aegean and Western Turkey sclerophyllous and mixed forests" WWF scientific report. Accessed May 25 2008 [7]
- ↑ "Southern Anatolian montane conifer and deciduous forests" WWF scientific report. Accessed May 25 2008 [8]
- ↑ "SEastern Mediterranean conifer-sclerophyllous-broadleaf forests" WWF scientific report. Accessed May 25, 2008 http://www.worldwildlife.org/wildworld/profiles/terrestrial/pa/pa1207_full.html]
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Freeman, Charles (1999). Egypt, Greece and Rome: Civilizations of the Ancient Mediterranean. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0198721943.
- ↑ Howgego, C. J. (1995). Ancient History from Coins. ISBN 0415089921.
- ↑ Asia Minor Coins - an index of Greek and Roman coins from Asia Minor (ancient Anatolia)
- ↑ Justin McCarthy,"Death and Exile: The Ethnic Cleansing of Ottoman Muslims, 1821-1922",1996,ISBN-10: 0878500944
See also
- Anatolianism
- History of Anatolia
- Anatolian Turkish Beyliks
- 1268 Cilicia earthquake
- Anatolian Bulgarians
- Ancient Greece
- Armenia
- Byzantine Empire
- Caria
- Cilicia
- Etruscans
- Hittites
- Zaza people
- Kurd
- Lazs
- Lycia
- Lydia
- Ottoman Empire
- Pamphylia
- Phrygia
- Pontus
- Saint Anatolia, Roman Catholic Saint
- Seljuk Sultanate of Rûm
- Turkey
- Turkish Riviera
External links
|
|||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||


