Ash Wednesday
| Ash Wednesday | |
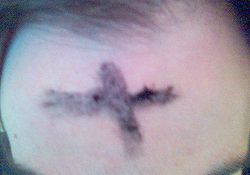 A cross of ashes on a worshipper's forehead on Ash Wednesday |
|
| Observed by | Western Christians |
|---|---|
| Type | Christian |
| Date | As early as February 4 to as late as March 10 |
| 2008 date | February 6 |
| 2009 date | February 25 |
| 2010 date | February 17 |
| Observances | Service of worship or Mass Marking of an ash cross on the forehead |
| Related to | Shrove Tuesday/Mardi Gras Lent Easter |
| Liturgical year |
|---|
| Western |
|
| Eastern |
|
In the Western Christian calendar, Ash Wednesday is the first day of Lent and occurs forty days before Easter (excluding Sundays). It falls on a different date each year, because it is dependent on the date of Easter; it can occur as early as February 4 or as late as March 10.
Ash Wednesday gets its name from the practice of placing ashes on the foreheads of the faithful as a sign of repentance. The ashes used are gathered after the Palm Crosses from the previous year's Palm Sunday are burned. In the liturgical practice of some churches, the ashes are mixed with the Oil of the Catechumens[1] (one of the sacred oils used to anoint those about to be baptized), though some churches use ordinary oil. This paste is used by the clergyman who presides at the service to make the sign of the cross, first upon his own forehead and then on each of those present who kneel before him at the altar rail. As he does so, he recites the words: "Remember (O man) that you are dust, and to dust you shall return."
Contents |
Ritual
At Masses and services of worship on this day, ashes are imposed on the foreheads of the faithful (or on the tonsure spots, in the case of some clergy). The priest, minister, or in some cases officiating layperson, marks the forehead of each participant with black ashes in the shape of a cross, which the worshipper traditionally retains until washing it off after sundown. The act echoes the ancient Near Eastern tradition of throwing ashes over one's head to signify repentance before God (as related in the Bible). The priest or minister says one of the following when applying the ashes:
Remember, O man, that you are dust, and unto dust you shall return. (Latin: Memento homo, quia pulvis es, et in pulverem reverteris.)
Turn away from sin and be faithful to the Gospel.
Repent, and hear the good news.

The ashes used in the service of worship or Mass are sacramentals, not a sacrament. The ashes are blessed according to various rites proper to each liturgical tradition, sometimes involving the use of Holy Water. In some churches they are mixed with light amounts of water[2] or olive oil[3][4], which serve as a fixative.
In most liturgies for Ash Wednesday, the Penitential psalms are read; Psalm 51 (LXX Psalm 50) is especially associated with this day.[5] The service also often includes a corporate confession rite.
In some of the free church liturgical traditions, other practices are sometimes added or substituted, as other ways of symbolizing the confession and penitence of the day. For example, in one common variation, a small card or piece of paper is distributed to the congregation on which a person is invited to write a sin she/he wishes to confess. These small cards are brought forth to the altar table where they are burned.[6]
In the Roman Catholic Church, ashes, being sacramentals, may be given to any Christian [7][8] as opposed to Catholic sacraments, which are generally reserved for church members, except in cases of grave necessity.[9][10] Similarly, in most other Christian denominations ashes may be received by all who profess the Christian faith and are baptized.[11]
In the Roman Catholic Church, Ash Wednesday is observed by fasting, abstinence from meat, and repentance—a day of contemplating one's transgressions. The Anglican Book of Common Prayer also designates Ash Wednesday as a day of fasting. In other Christian denominations these practices are optional, with the main focus being on repentance. On Ash Wednesday and Good Friday, Roman Catholics between the ages of 18 and 59 are permitted to consume only one full meal, which may be supplemented by two smaller meals, which together should not equal the full meal. Some Roman Catholics will go beyond the minimum obligations demanded by the Church and undertake a complete fast or a bread and water fast. Ash Wednesday and Good Friday are also days of abstinence from meat (for those Catholics age 14 and over), as are all Fridays in Lent. Some Roman Catholics continue fasting during the whole of Lent, as was the Church's traditional requirement, concluding only after the celebration of the Easter Vigil.
As the first day of Lent, it comes the day after Shrove Tuesday or Mardi Gras (Fat Tuesday), the last day of the Carnival season.[12]
Biblical significance
Ash Wednesday is a day of repentance and it marks the beginning of Lent. Ashes were used in ancient times, according to the Bible, to express mourning. Dusting oneself with ashes was the penitent's way of expressing sorrow for sins and faults. An ancient example of one expressing one's penitence is found in Job 42:3-6. Job says to God: "I have heard of thee by the hearing of the ear: but now mine eye seeth thee. Wherefore I abhor myself, and repent in dust and ashes." (vv. 5-6, KJV) Other examples are found in several other books of the Bible including, Numbers 19:9, 19:17, Jonah 3:6, Matthew 11:21, and Luke 10:13, and Hebrews 9:13.
However, some Christians who do not celebrate Ash Wednesday say that the practice is not consistent with Scripture and is of pagan origin.[13] They usually cite Matthew 6:16–18, where Jesus gave prescriptions for fasting: "And whenever you fast, do not look dismal, like the hypocrites. Truly I tell you, they have received their reward. But when you fast, put oil on your head and wash your face, so that your fasting may be seen not by others but by your Father who is in secret; and your Father who sees in secret will reward you." (NRSV) These groups argue that Jesus warned against fasting to gain favor from other people and that he also warned his followers that they should fast in private, not letting others know they were fasting. For these reasons, some Christian denominations do not endorse the practice. Others, however, point out that this very passage from Matthew is the one, not coincidentally, that is appointed by the Revised Common Lectionary to be read on Ash Wednesday. They might also clarify that the ashen Cross on the forehead does not represent the fast, but the mortal (fallen) condition of human existence. And they would refer to Jesus' words whereby he expected people to repent using sackcloth and ashes: "Woe to you, Korazin! Woe to you, Bethsaida! For if the miracles that were performed in you had been performed in Tyre and Sidon, they would have repented long ago, sitting in sackcloth and ashes." (Luke 10:13; see also Matthew 11:21)
Dates
Ash Wednesday is a moveable feast, falling exactly 46 days before Easter. It fell on February 6 in 2008. In future years Ash Wednesday will occur on these dates:
- 2009 - February 25
- 2010 - February 17
- 2011 - March 9
- 2012 - February 22
- 2013 - February 13
- 2014 - March 5
- 2015 - February 18
- 2016 - February 10
- 2017 - March 1
- 2018 - February 14
- 2019 - March 6
Historical notes: The earliest date Ash Wednesday can occur is February 4 (in a common year with Easter on March 22), which happened in 1573, 1668, 1761 and 1818. The latest date is March 10 (when Easter Day falls on April 25) which occurred in 1546, 1641, 1736, 1886 and 1943. Ash Wednesday has never occurred on Leap Year Day (February 29), which will not happen until 2096; the only other years the third millennium will have Ash Wednesday on February 29 are 2688, 2840, and 2992. (Ash Wednesday falls on Feb. 29 if Easter is April 15 in leap year.)
Denominations observing Ash Wednesday
These Christian denominations are among those that mark Ash Wednesday by holding a service of worship or Mass:
- African Methodist Episcopal Church
- African Methodist Episcopal Zion Church
- Anglican/Episcopal churches (excepting most Sydney Diocese churches)
- Individual Baptist churches may hold a service
- Church of God (Anderson)
- Church of the Nazarene
- Some congregations of Community of Christ
- Some Free Churches
- The Liberal Catholic Church
- Lutheran churches
- Old Catholic Church
- Reformed churches (Presbyterian, United Church of Christ, Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), etc.)
- Roman Catholic Church
- United Methodist churches
- Wesleyan churches
The Eastern Orthodox Church does not in general observe Ash Wednesday; instead, Orthodox Great Lent begins on Clean Monday. There are, however, a relatively small number of Orthodox Christians who follow the Western Rite; these do observe Ash Wednesday, although often on a different day from the previously-mentioned denominations, as its date is determined from the Orthodox calculation of Pascha, which may be as much as a month later than the Western observance of Easter.
See also
- Holy Week - the last week in the season of Lent
- Carnival festival ending on Ash Wednesday
- Ash Wednesday (poem) a poem by T.S. Eliot
- Ash Wednesday (album) by Elvis Perkins
References
- ↑ This ties the beginning of Lent with its original purpose: the final preparation of Catechumens for baptism.
- ↑ Ford, Penny. "Lent 101". Upper Room Ministries.
- ↑ Real Live Preacher: Ash Wednesday
- ↑ "Lent and Easter". The Diocese of London (2004-03-17).
- ↑ Psalm 51 is the Ash Wednesday reading in both the Revised Common Lectionary and The Roman Catholic Lectionary.
- ↑ "What is the significance of ashes being placed on the forehead on Ash Wednesday?". The United Methodist Church.
- ↑ "Responses to frequently asked questions regarding Lenten practices". Catholics United for the Faith.
- ↑ Code of Canon Law, canon 1170
- ↑ Donovan, Colin B.. "Communion of Non-Catholics or Intercommunion". Eternal Word Television Network.
- ↑ 1983 Code of Canon Law, canon 844
- ↑ "Pastor's Message: Ash Wednesday, An Invitation To Lent". First United Methodist Church (2001-02-28).
- ↑ The origin of the name "carnival" is disputed. One theory states that the word comes from the Late Latin expression carne vale, which means "farewell to meat", signifying that those were the last days when one could eat meat before the fasting of Lent. Other sources, however, suggest that the name comes from the Italian carne levare or similar expression, meaning "to remove meat", since meat is prohibited during Lent. According to the Oxford English Dictionary, the word "Carnival" is derived from Latin carnem levare (removal of the meat) or carnem laxare (leaving the meat).
- ↑ "Ash Wednesday: Is it in the Bible?". Bibleinfo.com. Seventh-day Adventist Church.
External links
- Lent: Ash Wednesday - All Saints' King's Lynn
- Catholic Encyclopedia: Ash Wednesday
- Reflections and history of Ash Wednesday
- An Episcopal Ash Wednesday Service
- The Text This Week: Ash Wednesday
- Upper Room Ministries: Biblical Significance of Ash Wednesday
- Dates of Ash Wednesday from 1583 - 9999
- Evangelical Ash Wednesday