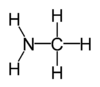
Amine

Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic substituents such as alkyl and aryl groups. Compounds with the nitrogen atom next to a carbonyl of the structure R-C(=O)NR2 are called the amides and have different chemical properties. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine and aniline; see Category:Amines for a list of amines.
Contents |
Introduction
Aliphatic Amines
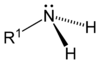
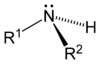
As displayed in the images below, primary amines arise when one of three hydrogen atoms in ammonia is replaced by an organic substituent. Secondary amines have two organic substituents bound to N together with one H. In tertiary amines all three hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic substituents. It is also possible to have four alkyl substituents on the nitrogen. These compounds have a charged nitrogen center, and necessarily come with a negative counterion, so they are called quaternary ammonium salts.
| Primary amine | Secondary amine | Tertiary amine |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
Similarly, an organic compound with multiple amino groups is called a diamine, triamine, tetraamine and so forth.
Aromatic amines
Aromatic amines have the nitrogen atom connected to an aromatic ring as in anilines. The aromatic ring strongly decreases the alkalinity of the amine, depending on its substituents. Interestingly, the presence of an amine group strongly increases the reactivity of the aromatic ring, due to an electron-donating effect. One organic reaction involving aromatic amines is the Goldberg reaction.
Naming conventions
- the prefix "N-" shows substitution on the nitrogen atom
- as prefix: "amino-"
- as suffix: "-amine"
Systematic names for some common amines:
| Lower amines are named with the suffix -amine.
|
Higher amines have the prefix amino as a functional group.
|
- Primary amines:
- methylamine
- ethanolamine or 2-aminoethanol
- trisamine (or more commonly tris) (Its HCl salt is used as a pH buffering agent in biochemistry)
- Secondary amines:
- dimethylamine
- methylethanolamine or 2-(methylamino)ethanol
- Cyclic amines:
- aziridine (3-member ring),
- azetidine (4-member ring),
- pyrrolidine (5-member ring) and
- piperidine (6-member ring)
- Tertiary amines:
- trimethylamine
- dimethylethanolamine (DMEA) or 2-(dimethylamino)ethanol
- bis-tris (It is used as a pH buffering agent in biochemistry)
Physical properties
General properties
- Hydrogen bonding significantly influences the properties of primary and secondary amines as well as the protonated derivatives of all amines. Thus the boiling point of amines is higher than those of the corresponding phosphines, but generally lower than those of the corresponding alcohols. Alcohols, or alkanols, resemble amines but feature an -OH group in place of NR2. Since oxygen is more electronegative than nitrogen, RO-H is typically more acidic than the related R2N-H compound.
- Methyl-, dimethyl-, trimethyl-, and ethylamine are gases under standard conditions, whereas diethylamine and triethylamine are liquids. Most other common alkyl amines are liquids; high-molecular-weight amines are, of course, solids.
- Gaseous amines possess a characteristic ammonia smell, liquid amines have a distinctive "fishy" smell.
- Most aliphatic amines display some solubility in water, reflecting their ability to form hydrogen bonds. Solubility decreases with the increase in the number of carbon atoms, especially when the carbon atom number is greater than 6.
- Aliphatic amines display significant solubility in organic solvents, especially polar organic solvents. Primary amines react with ketones such as acetone, and most amines are incompatible with chloroform and carbon tetrachloride.
- The aromatic amines, such as aniline, have their lone pair electrons conjugated into the benzene ring, thus their tendency to engage in hydrogen bonding is diminished. Otherwise they display the following properties:
- Their boiling points are usually still high due to their larger size.
- Diminished solubility in water, although they retain their solubility in suitable organic solvents only.
- They are toxic and are easily absorbed through the skin: thus hazardous.
Chirality
Tertiary amines of the type NHRR' and NRR'R" are chiral: the nitrogen atom bears four distinct substituents counting the lone pair. The energy barrier for the inversion of the stereocenter is relatively low, e.g., ~7 kcal/mol for a trialkylamine. The interconversion of the stereoisomers has been compared to the inversion of an open umbrella in to a strong wind. Because of this low barrier, amines such as NHRR' cannot be resolved optically and NRR'R" can only be resolved when the R, R', and R" groups are constrained in cyclic structures such as aziridines. Quaternary ammonium salts with four distinct groups on the nitrogen are capable of exhibiting optical activity.
Properties as bases
Like ammonia, amines act as bases but are reasonably weak(see table for examples of conjugate acid Ka values). The basicity of amines depends on:
- The electronic properties of the substituents (alkyl groups enhance the basicity, aryl groups diminish it).
- Steric hindrance offered by the groups on nitrogen.
- The degree of solvation of the protonated amine.
The nitrogen atom features a lone electron pair that can bind H+ to form an ammonium ion R3NH+. The lone electron pair is represented in this article by a two dots above or next to the N. The water solubility of simple amines is largely due to hydrogen bonding between protons on the water molecules and these lone electron pairs.
- Inductive effect of alkyl groups
| Ions of compound | Kb |
|---|---|
| Ammonia NH3 | 1.8·10-5 M |
| Methylamine CH3NH2 | 4.4·10-4 M |
| propylamine CH3CH2CH2NH2 | 4.7·10-4 M |
| 2-propylamine (CH3)2CHNH2 | 5.3·10-4 M |
| dimethylamine (CH3)2NH | 5.4·10-4 M |
| trimethylamine (CH3)3N | 5.9·10-5 M |
- +I effect of alkyl groups raises the energy of the lone pair of electrons, thus elevating the basicity. Thus the basicity of an amine may be expected to increase with the number of alkyl groups on the amine. However, there is no strict trend in this regard, as basicity is also governed by other factors mentioned above. Consider the Kb values of the methyl amines given above. The increase in Kb from methylamine to dimethylamine may be attributed to +I effect; however, there is a decrease from dimethylamine to trimethyl amine due to the predominance of steric hindrance offered by the three methyl groups to the approaching Lewis acid.
- Mesomeric effect of aromatic systems
| Ions of compound | Kb |
|---|---|
| Ammonia NH3 | 1.8·10-5 M |
| Aniline C6H5NH2 | 3.8·10-10 M |
| 4-methylphenylamine 4-CH3C6H4NH2 | 1.2·10-9 M |
| 2-nitrophenylamine | 1.5·10-15 M |
| 3-nitrophenylamine | 2.8·10-13 M |
| 4-nitrophenylamine | 9.5·10-14 M |
- -M effect of aromatic ring delocalises the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen into the ring, resulting in decreased basicity. Substituents on the aromatic ring, and their positions relative to the amine group may also considerably alter basicity as seen above.
- The degree of solvation of protonated amines:
| Ions of compound | Maximum number of H-bond |
|---|---|
| NH4+ | 4 Very Soluble in H2O |
| RNH3+ | 3 |
| R2NH2+ | 2 |
| R3NH+ | 1 Least Soluble in H2O |
The degree of solvation of the protonated amine depends on the approachability of solvent molecules. If the molecule is sterically hindered (as in the case of trimethylamine), the protonated form is not well-solvated, thereby reducing basicity. This also explains the order of basicity of the methyl amines (see above). In the case of aprotic polar solvents (like DMSO and DMF), wherein the extent of solvation is not as high as in protic polar solvents (like water and methanol), the basicity of amines is almost solely governed by the electronic factors within the molecule.
Synthesis
The following laboratory methods exist for the preparation of amines:
- via the Gabriel synthesis:
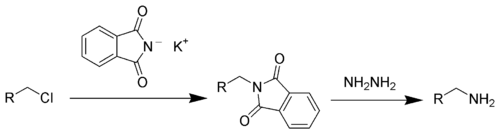
- via azides by the Staudinger reduction, or with a reducing agent such as lithium aluminium hydride.
- From carboxylic acids in the Schmidt reaction.
- Allylic amines can be prepared from imines in the Aza-Baylis-Hillman reaction.
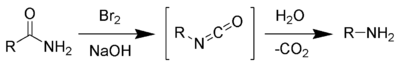
- via Hofmann degradation of amides. This reaction is valid for preparation of primary amines only. Gives good yields of primary amines uncontaminated with other amines.
- Quaternary ammonium salts upon treatment with strong base undergo the so-called Hofmann Elimination
- Reduction of nitriles, amides and nitro compounds:
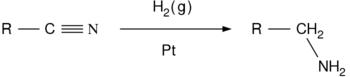
- Nitriles are reduced to amines using hydrogen in the presence of a nickel catalyst, although acidic or alkaline conditions should be avoided to avoid hydrolysis of -CN group. LiAlH4 is more commonly employed for the reduction of nitriles on the laboratory scale. Similarly, LiAlH4 reduces amides to amines:
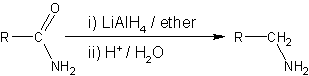
- The reduction of nitro compounds to amines can be accomplished with elemental zinc, tin or iron with an acid.
-
For more details on this topic, see Reduction of nitro compounds.
- Nucleophilic substitution of haloalkanes [1]. Primary amines can also be synthesized by alkylaton of ammonia. Haloalkanes react with amines to give a corresponding alkyl-substituted amine, with the release of a halogen acid. Such reactions, which are most useful for alkyl iodides and bromides, are rarely employed because the degree of alkylation is difficult to control. If the reacting amine is tertiary, a quaternary ammonium cation results in the Menshutkin reaction. Many quaternary ammonium salts can be prepared by this route with diverse R groups and many halide and pseudohalide anions.
- via halides and hexamine in the Delepine reaction
- aryl amines can be obtained from amines and aryl halides in the Buchwald-Hartwig reaction
- from alkenes and alkynes in hydroamination
- from rearrangement of haloamines in the Hofmann-Löffler reaction
- via amination of an alcohol with ammonia over a hydrogenating catalyst such as a nickel/copper alloy.[2]
Reactions
Amines react in a variety of ways:
- By nucleophilic acyl substitution. Acyl chlorides and acid anhydrides react with primary and secondary amines in cold to form amides in the Schotten-Baumann reaction. Tertiary amines cannot be acylated due to the absence of a replaceable hydrogen atom. With the much less active benzoyl chloride, acylation can still be performed by the use of excess aqeous alkali to facilitate the reaction.
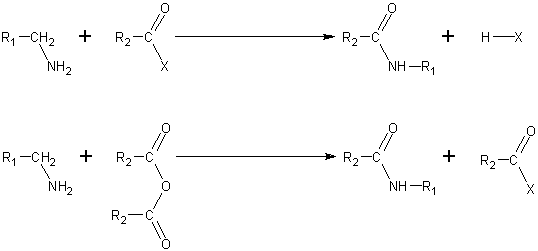
- Because amines are basic, they neutralize carboxylic acids to form the corresponding ammonium carboxylate salts. Upon heating to 200 °C, the primary and secondary amine salts dehydrate to form the corresponding amides.
- By ammonium salt formation. Amines R3N react with strong acids such as hydroiodic acid, hydrobromic acid and hydrochloric acid in neutralization reactions forming ammonium salts R3NH+.
- By diazonium salt formation. Nitrous acid with formula HNO2 is unstable, therefore usually a mixture of NaNO2 and dilute hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid is used to produce nitrous acid indirectly. Primary aliphatic amines with nitrous acid give very unstable diazonium salts which spontaneously decompose by losing N2 to form carbonium ion. The carbonium ion goes on to produce a mixture of alkenes, alkanols or alkyl halides, with alkanols as the major product. This reaction is of little synthetic importance because the diazonium salt formed is too unstable, even at cold conditions.
- NaNO2 + HCl → HNO2 + NaCl
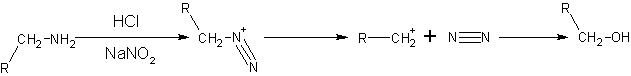
- Primary aromatic amines, such as aniline (phenylamine) form more stable diazonium ions at 0–5 °C. Above 5 °C, they will decompose to give phenol and N2. Arenediazonium salts can be isolated in the crystalline form but are usually used in solution immediately after preparation, due to rapid decomposition on standing even when cold. The solid arenediazonium salt is explosive upon shock or mild warming. Because of their greater stability, arenediazonium salts are more synthetically useful than their aliphatic counterparts. Since it is not necessary to isolate the diazonium salt, once it is formed another reagent such as cuprous cyanide can simply be added to the mixture, and with gentle heating of the solution, a replacement reaction takes place along with the evolution of nitrogen. In addition, arenediazonium ions can also undergo a coupling reaction with a highly activated aromatic compound such as a phenol to form an azo compound.
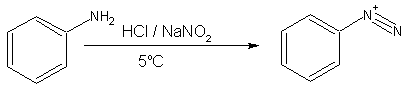
- By imine formation. Primary amines react with ketones and aldehydes to form imines. In the case of formaldehyde (R' = H), these products are typically cyclic trimers.
- RNH2 + R'2C=O → R'2C=NR + H2O
- Secondary amines react with ketones and aldehydes to form enamines
- R2NH + R'(R"CH2)C=O → R"CH=C(NR2)R' + H2O
- By oxidation to nitroso compounds, for instance with peroxymonosulfuric acid.
- By reduction of quaternary ammonium cations to tertiary amines in the Emde degradation.
- By rearrangement of N-alkyl anilines to aryl substituted anilines in the Hofmann-Martius rearrangement.
- primary and secondary amines react with pyridinium salts in the Zincke reaction
- By cleavage (tertiary amines only) with cyanogen bromide in the Von Braun reaction.
Biological activity
Amines have strong, characteristic odors, and are toxic. The smells of ammonia, old fish, urine, rotting flesh, and semen are all mainly composed of amines. Many kinds of biological activity produce amines by breakdown of amino acids.
Use of amines
Dyes
Primary aromatic amines are used as a starting material for the manufacture of azo dyes. It reacts with nitric(III) acid to form diazonium salt, which can undergo coupling reaction to form azo compound. As azo-compounds are highly coloured, they are widely used in dyeing industries, such as:
- Methyl orange
- Direct brown 138
- Sunset yellow FCF
- Ponceau
Drugs
- Chlorpheniramine is an antihistamine with hundreds of trade names including Chlor-Trimeton that helps to relieve allergic disorders due to cold, hay fever, itchy skin, insect bites and stings. It is the most familiar of a series of antihistamines which include pheniramine (Naphcon), brompheniramine (Dimetapp), fluorpheniramine and iodopheniramine (experimental), dexchlorpheniramine (Polaramine), dexbrompheniramine (Drixoral), deschlorpheniramine, and many others. These drugs, particularly chlorpheniramine and dexchlorpheniramine, are also being examined for their anti-depressant potential. The antihistamines of this group are frequently used alongside opioids for pain and coughing to reduce side effects, possibly reduce the dose of the opioid needed to have a given effect, and boost the positive effects of both drugs. Various hydrocodone, dihydrocodeine, and codeine cough syrups contain chlorpheniramine for this reason, and chlorpheniramine or one of its relatives are sometimes prescribed or recommended for use on top of paracetamol-and-codeine mixtures like Tylenol With Codeine, hydrocodone, dihydrocodeine and other pain relievers, with the "stack" of a narcotic pain reliever, ibuprofen or naproxen, chlorpheniramine, and orphenadrine being a common part of treatment of low-back pain, sports injuries, and painful symptoms related to mensturation.
- Chlorpromazine is a tranquilliser that sedates without inducing sleep. It is used to relieve anxiety, excitement, restlessness or even mental disorder. It has many chemical relatives which include many antihistamines, major tranquillisers, sedatives for small and medium-seized animals as well as a potentiator in opioid-based drug formulations used in darts to knock out large animals, anti-nauseants, and agents to improve metabolism of other drugs.
- Ephedrine and Phenylephrine, as amine hydrochlorides, are used as decongestants.
- Amphetamine, Methamphetamine, and Methcathinone are amines that are listed as controlled substances by the DEA.
- Amitriptyline, Imipramine, Lofepramine and Clomipramine are tricyclic antidepressants and tertiary amines
- Nortriptyline, Desipramine, and Amoxapine are tricyclic antidepressants and secondary amines
- (The tricyclics are grouped by the nature of the final amine group on the side chain.)
Gas Treatment
- Aqueous monoethanolamine (MEA), diglycolamine (DGA), diethanolamine (DEA), diisopropanolamine (DIPA) and methyldiethanolamine (MDEA) are widely used industrially for removing carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen sulfide (H2S) from natural gas streams and refinery process streams. They may also be used to remove CO2 from combustion gases / flue gases and may have potential for abatement of greenhouse gases.
See also
|
|
References
- ↑ For an example see: Org. Synth. 2008, 85, 10-14 Article
- ↑ http://www.freepatentsonline.com/4014933.html,"Production of Amines from Alcohols"
|
|||||