Christianity
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Religion; Religious movements, traditions and organizations
Christianity is a monotheistic religion centered on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth as presented in the New Testament. Christians believe Jesus to be the Son of God and the Messiah prophesied in the Old Testament. With an estimated 2.1 billion adherents in 2001, Christianity is the world's largest religion. It is the predominant religion in Europe, the Americas, Southern Africa, the Philippine Islands and Oceania. It is also growing rapidly in Asia, particularly in China and South Korea.
Christianity shares its origins and many religious texts with Judaism, specifically the Hebrew Bible, known to Christians as the Old Testament. Like Judaism and Islam, Christianity is classified as an Abrahamic religion (see also, Judeo-Christian).
The name "Christian" ( Greek Χριστιανός Strong's G5546), meaning "belonging to Christ" or "partisan of Christ", was first applied to the disciples in Antioch, as recorded in Acts 11:26. The earliest recorded use of the term "Christianity" (Greek Χριστιανισμός) is by Ignatius of Antioch.
| Contents |
|---|
|
|
Beliefs
Although Christianity has always had a significant diversity of belief, most Christian branches and denominations share a common set of doctrines that they hold as essential to their faith.
Jesus Christ
As indicated by the name "Christianity", the focus of Christian theology is a belief in Jesus as the Messiah or Christ. The title "Messiah" comes from the Hebrew word מָשִׁיחַ (māšiáħ) meaning "the anointed one" or "King." The Greek translation Χριστός (Christos) is the source of the English word Christ.
Christians believe that, as the Messiah, Jesus was anointed as ruler and savior of humanity, and hold that Jesus's coming was the fulfilment of messianic prophecies of the Old Testament. The Christian concept of the Messiah differs significantly from the contemporary Jewish concept. The core Christian belief is that, through the death and resurrection of Jesus, the perfect Son of God, mankind is reconciled to God and thereby attains salvation by grace and the promise of eternal life to all who trust in Christ. The need for salvation was caused by original sin.
While there have been theological disputes over the nature of Jesus, most Christians believe that Jesus is God incarnate and " true God and true man" (or both fully divine and fully human). Jesus, having become fully human in all respects, including the aspect of mortality, suffered the pains and temptations of mortal man, yet he did not sin. As fully God, he defeated death and rose to life again. According to the Bible, "God raised him from the dead", he ascended to heaven, to the "right hand of God", and will return again to fulfil the rest of Messianic prophecy such as the Resurrection of the dead, the Last Judgment and establishment of the Kingdom of God (See also Messianism and Messianic Age).
According to the Gospels, Jesus was conceived by the Holy Spirit and born from the the virgin Mary. Little of Jesus' childhood is recorded in the Gospels compared to his adulthood, especially the week before his death. The Biblical accounts of Jesus' ministry include his baptism, miracles, teachings and deeds.
Death and Resurrection
Most Christians consider the death of Jesus, followed by his resurrection, the cornerstone of their faith and the most important event in history.
According to the Gospels, Jesus and his followers went to Jerusalem the week of the Passover where they were eagerly greeted by a crowd. In Jerusalem, Jesus cleansed the Temple, and predicted its destruction - heightening conflict with the Jewish authorities who were plotting his death.
After sharing his last meal with his disciples, Jesus went to pray in the Garden of Gethsemane where he was betrayed by his disciple Judas Iscariot and arrested by the temple guard on orders from the Sanhedrin and the high priest Caiaphas. Jesus was convicted by the Sanhedrin of blasphemy and transferred to the Roman governor Pilate, who had him crucified for inciting rebellion. Jesus died by late afternoon and was entombed.
Christians believe that God raised Jesus from the dead on the third day, that Jesus appeared to his apostles and other disciples, commissioned his disciples to "make disciples of all nations, baptizing them in the name of the Father and of the Son (Jesus) and of the Holy Spirit." and ascended to heaven. Christians also believe that God sent the disciples the Holy Spirit (or Paraclete).
Salvation
Christians believe salvation is a gift by unmerited grace of God, who sent Jesus as the savior. Christians believe that through faith in Jesus one can be saved from sin and spiritual death. The crucifixion of Jesus is explained as an atoning sacrifice, which, in the words of the Gospel of John, "takes away the sins of the world". Reception of salvation is related to justification.
The operation and effects of grace are understood differently by different traditions. Catholicism and Eastern Orthodoxy teach the necessity of the free will to cooperate with grace. Reformed theology places distinctive emphasis on grace by teaching that mankind is completely incapable of self-redemption, but the grace of God overcomes even the unwilling heart.
The Trinity
Most Christians believe that God is spirit ( John 4:24), an uncreated, omnipotent and eternal being, the creator and sustainer of all things, who works the redemption of the world through his Son, Jesus Christ.
Against this background, belief in the divinity of Christ and the Holy Spirit was expressed as the doctrine of the Holy Trinity,, which describes the single Divine substance existing as three distinct and inseparable persons: the Father, the Son (Jesus Christ the eternal Word), and the Holy Spirit. According to the doctrine, God is not divided in the sense that each person has a third of the whole; rather, each person is considered to be fully God (see Perichoresis). The distinction lies in their relations, the Father being unbegotten, the Son begotten of the Father, and the Holy Spirit proceeding. "Begotten", in these formulae, does not refer to Mary's conceiving Jesus, but to the Son's relationship to the Father, which is described as being "eternally begotten" of the Father.
Trinitarian Christian also conceive of salvation as one work of the triune God, in which "the three divine persons act together as one, and manifest their own proper characteristics."
Trinitarian Christians trace the orthodox formula of the Trinity — Father, Son, and Holy Spirit — back to the resurrected Jesus himself, who used this phrase in the Great Commission ( Matthew 28:16-20).
Most Christians believe the Holy Spirit inspired the Scriptures, and that his active participation in a believer's life (even to the extent of "indwelling" within the believer), joining the believer's free actions with his own, is essential to living a Christian life. In Catholic, Orthodox, and some Anglican theology, this indwelling is received through the sacrament called Confirmation or, in the East, Chrismation. Most Protestant traditions teach that the gift of the Holy Spirit is symbolized by baptism; however some (Baptists and comparable groups) do not attribute any sacramental significance to baptism. Pentecostal and Charismatic Protestants believe the baptism with the Holy Spirit is a distinct experience separate from other experiences like conversion or water baptism, and many Pentecostals believe it will always—or at least usually—be evident through glossolalia (speaking in tongues).
Non-Trinitarians
In antiquity, and again following the Reformation, several sects advocated views contrary to the Trinity. These views were rejected by many bishops such as Irenaeus and subsequently by the Ecumenical Councils. During the Reformation, though most Catholics, Orthodox, and Protestants accepted the value of many of the Councils, some groups rejected these councils as spiritually tainted. Clement Ziegler, Casper Schwenckfeld, and Melchior Hoffman advanced the view that Christ was only divine and not human. Michael Servetus denied the divinity of Christ, as did others who were tried at Augsburg in 1527.
Modalists, such as Oneness Pentecostals, regard God as a single person, with the Father, Son, and Holy Spirit considered modes or roles by which the unipersonal God expresses himself.
Latter-day Saints accept the divinity of the Father, Son, and Holy Spirit, but deny that they are the same being, believing them to be separate beings united only in will and purpose.
Present day groups who do not consider Jesus to be God include Unitarians, descendants of Reformation era Socinians and Jehovah's Witnesses.
Scriptures
Christianity regards the Bible, a collection of canonical books in two parts, the Old Testament and the New Testament, as authoritative: written by human authors under the inspiration of the Holy Spirit and therefore inerrant. Protestants believe that the scriptures contain all revealed truth necessary for salvation (See Sola scriptura).
The Old Testament contains the entire Jewish Tanakh, though in the Christian canon the books are ordered differently and some books of the Tanakh are divided into several books by the Christian canon. The Catholic and Orthodox canons include the Hebrew Jewish canon and other books (from the Septuagint Greek Jewish canon) which Catholics call Deuterocanonical, while Protestants consider them Apocrypha.
The first four books of the New Testament are the Gospels ( Matthew, Mark, Luke and John), which recount the life and teachings of Jesus. The first three are often called synoptic because of the amount of material they share. The rest of the New Testament consists of a sequel to Luke's Gospel, the Acts of the Apostles, which describes the very early history of the Church, a collection of letters from early Christian leaders to congregations or individuals, the Pauline and General epistles, and the apocalyptic Book of Revelation.
Some traditions maintain other canons. The Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church maintains two canons, the Narrow Canon, itself larger than any Biblical canon outside Ethiopia, and the Broad Canon, which has even more books.The Latter-day Saints hold the Bible and three additional books to be the inspired word of God: the Book of Mormon, the Doctrine and Covenants, and the Pearl of Great Price.
Interpretation
Though Christians largely agree on the content of the Bible, there is significant divergence in its interpretation, or exegesis. In antiquity, two schools of exegesis developed in Alexandria and Antioch. Alexandrine interpretation, exemplified by Origen, tended to read Scripture allegorically, while Antiochene interpretation adhered to the literal sense, holding that other meanings (called theoria) could only be accepted if based on the literal meaning.
Catholic theology distinguishes two senses of scripture: the literal and the spiritual, the latter being subdivided into the allegorical, moral, and anagogical senses. The literal sense is "the meaning conveyed by the words of Scripture and discovered by exegesis, following the rules of sound interpretation." The allegorical sense includes typology, for example the parting of the Red Sea is seen as a "type" of or sign of baptism; the moral sense contains ethical teaching; the anagogical sense includes eschatology and applies to eternity and the consummation of the world. Catholic theology also adds other rules of interpretation, which include the injunction that all other senses of sacred scripture are based on the literal, that the historicity of the Gospels must be absolutely and constantly held, that scripture must be read within the "living Tradition of the whole Church", and that "the task of interpretation has been entrusted to the bishops in communion with the successor of Peter, the Bishop of Rome."
Many Protestants stress the literal sense or historical-grammatical method, even to the extent of rejecting other senses altogether. Martin Luther advocated "one definite and simple understanding of Scripture". Other Protestant interpreters make use of typology. Protestants characteristically believe that ordinary believers may reach an adequate understanding of Scripture because Scripture itself is clear (or "perspicuous"), because of the help of the Holy Spirit, or both. Martin Luther believed that without God's help Scripture would be "enveloped in darkness", but John Calvin wrote, "all who refuse not to follow the Holy Spirit as their guide, find in the Scripture a clear light." The Second Helvetic Confession said, "we hold that interpretation of the Scripture to be orthodox and genuine which is gleaned from the Scriptures themselves (from the nature of the language in which they were written, likewise according to the circumstances in which they were set down, and expounded in the light of like and unlike passages and of many and clearer passages)." The writings of the Church Fathers, and decisions of Ecumenical Councils, though "not despise[d]", were not authoritative and could be rejected.
Creeds
Creeds, or concise doctrinal statements, began as baptismal formulas and were later expanded during the Christological controversies of the fourth and fifth centuries. The earliest creeds still in common use are the Apostles' Creed ( text in Latin and Greek, with English translations) and Paul's creed of 1 Cor 15:1-9.
The Nicene Creed, largely a response to Arianism, was formulated at the Councils of Nicaea and Constantinople in 325 and 381 respectively, and ratified as the universal creed of Christendom by the Council of Ephesus in 431.
The Chalcedonian Creed, developed at the Council of Chalcedon in 451, (though not accepted by the Oriental Orthodox Churches) taught Christ "to be acknowledged in two natures, inconfusedly, unchangeably, indivisibly, inseparably": one divine and one human, that both natures are perfect but are nevertheless perfectly united into one person.
The Athanasian Creed ( English translations), received in the western Church as having the same status as the Nicene and Chalcedonian, says: "We worship one God in Trinity, and Trinity in Unity; neither confounding the Persons not dividing the Substance."
Most Protestants accept the Creeds. Some Protestant traditions believe Trinitarian doctrine without making use of the Creeds themselves, while other Protestants, like the Restoration Movement, oppose the use of creeds.
Eschaton and afterlife
Most Christians believe that upon the death of the body, the individual soul, which is considered to be immortal, experiences the particular judgment and is either rewarded with heaven or condemned to hell. The elect are called "saints" (Latin sanctus: "holy") and the process of being made holy is called sanctification. In Catholicism, those who die in a state of grace but with either unforgiven venial sins or incomplete penance undergo purification in purgatory to achieve the holiness necessary for entrance into heaven.
At the last coming of Christ, the eschaton or end of time, all who have died will be resurrected bodily from the dead for the Last Judgement, whereupon Jesus will fully establish the Kingdom of God in fulfillment of scriptural prophecies.
Some groups do not distinguish a particular judgment from the general judgment at the end of time, teaching instead that souls remain in stasis until this time (see Soul sleep). These groups, and others that do not believe in the intercession of saints, generally do not employ the word "saint" to describe those in heaven. Universalists hold that eventually all will experience salvation, thereby rejecting the concept of an eternal hell for those who are not saved.
Worship and practices
Christian life

Christians believe that all people should strive to follow Christ in their everyday actions. For many, this includes obedience to the Ten Commandments This love includes such injunctions as "feed the hungry" and "shelter the homeless", and applies to friend and enemy alike. Though the relationship between charity and religious practice are sometimes taken for granted today, as Martin Goodman has observed, "charity in the Jewish and Christian sense was unknown to the pagan world." Other Christian practices include acts of piety such as prayer and Bible reading.
Christianity teaches that one can only overcome sin through divine grace: moral and spiritual progress can only occur with God's help through the gift of the Holy Spirit dwelling within the believer. Christians believe that by sharing in Christ's life, death, and resurrection, and by believing in Christ, they become dead to sin and are resurrected to a new life with Him.
Liturgical worship
Justin Martyr described second century Christian liturgy in his First Apology (c. 150) to Emperor Antoninus Pius, and his description remains relevant to the basic structure of Christian liturgical worship:
- "And on the day called Sunday, all who live in cities or in the country gather together to one place, and the memoirs of the apostles or the writings of the prophets are read, as long as time permits; then, when the reader has ceased, the president verbally instructs, and exhorts to the imitation of these good things. Then we all rise together and pray, and, as we before said, when our prayer is ended, bread and wine and water are brought, and the president in like manner offers prayers and thanksgivings, according to his ability, and the people assent, saying Amen; and there is a distribution to each, and a participation of that over which thanks have been given, and to those who are absent a portion is sent by the deacons. And they who are well to do, and willing, give what each thinks fit; and what is collected is deposited with the president, who succours the orphans and widows and those who, through sickness or any other cause, are in want, and those who are in bonds and the strangers sojourning among us, and in a word takes care of all who are in need."
Thus, as Justin described, Christians assemble for communal worship on Sunday, the day of the resurrection, though other liturgical practices often occur outside this setting. Scripture readings are drawn from the Old and New Testaments, but especially the Gospels. Often these are arranged on an annual cycle, using a book called a lectionary. Instruction is given based on these readings, called a sermon, or homily. There are a variety of congregational prayers, including thanksgiving, confession, and intercession, which occur throughout the service and take a variety of forms including recited, responsive, silent, or sung. The Lord's Prayer, or Our Father, is regularly prayed. The Eucharist (also called Holy Communion, or the Lord's Supper) consists of a ritual meal of consecrated bread and wine, discussed in detail below. Lastly, a collection occurs in which the congregation donates money for the support of the Church and for charitable work.
Some groups depart from this traditional liturgical structure. A division is often made between " High" church services, characterized by greater solemnity and ritual, and " Low" services, but even within these two categories there is great diversity in forms of worship. Seventh-day Adventists meet on Saturday (the original Sabbath), while others do not meet on a weekly basis. Charismatic or Pentecostal congregations may spontaneously feel led by the Holy Spirit to action rather than follow a formal order of service, including spontaneous prayer. Quakers sit quietly until moved by the Holy Spirit to speak. Some Evangelical services resemble concerts with rock and pop music, dancing, and use of multimedia. For groups which do not recognize a priesthood distinct from ordinary believers the services are generally lead by a minister, preacher, or pastor. Still others may lack any formal leaders, either in principle or by local necessity. Some churches use only a cappella music, either on principle (e.g. many Churches of Christ object to the use of instruments in worship) or by tradition (as in Orthodoxy).
Worship can be varied for special events like baptisms or weddings in the service or significant feast days. In the early church Christians and those yet to complete initiation would separate for the Eucharistic part of the worship. In many churches today, adults and children will separate for all or some of the service to receive age-appropriate teaching. Such children's worship is often called Sunday school or Sabbath school (Sunday schools are sometimes held before rather than during services).
Sacraments
A sacrament is a Christian rite that is an outward sign of an inward grace, instituted by Christ to sanctify humanity. Catholic, Orthodox, and some Anglican Christians describe Christian worship in terms of seven sacraments: Baptism, Confirmation or Chrismation, Eucharist (communion), Penance (reconciliation), Anointing of the Sick (last rites), Holy Orders (ordination), and Matrimony. Many Protestant groups, following Martin Luther, recognize the sacramental nature of baptism and Eucharist, but not usually the other five in the same way, while other Protestant groups reject sacramental theology. Latter-day saint worship emphasizes the symbolic role of rites, calling some ordinances. Though not sacraments, Pentecostal, Charismatic, and Holiness Churches emphasize " gifts of the Spirit" such as spiritual healing, prophecy, exorcism, glossolalia (speaking in tongues), and laying on of hands where God's grace is mysteriously manifest.
Eucharist
The Eucharist (also called Holy Communion, or the Lord's Supper) is the part of liturgical worship that consists of a consecrated meal, usually bread and wine. Justin Martyr described the Eucharist as follows:
- "And this food is called among us Eukaristia [the Eucharist], of which no one is allowed to partake but the man who believes that the things which we teach are true, and who has been washed with the washing that is for the remission of sins, and unto regeneration, and who is so living as Christ has enjoined. For not as common bread and common drink do we receive these; but in like manner as Jesus Christ our Saviour, having been made flesh by the Word of God, had both flesh and blood for our salvation, so likewise have we been taught that the food which is blessed by the prayer of His word, and from which our blood and flesh by transmutation are nourished, is the flesh and blood of that Jesus who was made flesh."
Orthodox, Roman Catholics, Lutherans, and many Anglicans believe that the bread and wine become the body and blood of Christ (the doctrine of the Real Presence). Most other Protestants, especially Reformed, believe the bread and wine represent the body and blood of Christ. These Protestants may celebrate it less frequently, while in Catholicism the Eucharist is celebrated daily. Catholic and Orthodox view communion as indicating those who are already united in the church, restricting participation to their members not in a state of mortal sin. In some Protestant churches participation is by prior arrangement with a church leader. Other churches view communion as a means to unity, rather than an end, and invite all Christians or even anyone to participate.
Liturgical Calendar
In the New Testament Paul of Tarsus organised his missionary travels around the celebration of Pentecost. (Acts 20.16 and 1 Corinthians 16.8) This practice draws from Jewish tradition, with such feasts as the Feast of Tabernacles, the Passover, and the Jubilee. Today Catholics, Eastern Christians, and traditional Protestant communities frame worship around a liturgical calendar. This includes holy days, such as solemnities which commemorate an event in the life of Jesus or the saints, periods of fasting such as Lent, and other pious events such as memoria or lesser festivals commemorating saints. Christian groups that do not follow a liturgical tradition often retain certain celebrations, such as Christmas, Easter and Pentecost. A few churches make no use of a liturgical calendar.
Symbols
Today the best-known Christian symbol is the cross, which refers to the method of Jesus' execution. Several varieties exist, with some denominations tending to favour distinctive styles: Catholics the crucifix, Orthodox the crux orthodoxa, and Protestants an unadorned cross. An earlier Christian symbol was the ' ichthys' fish (Greek Alpha - α) symbol and anagram. Other text based symbols include ' IHS or ICXC' and ' chi-rho' (the first two letters of the word Christ in Greek). In a modern Roman alphabet, the Chi-Rho appears like an X (Chi - χ) with a large P (Rho - ρ) overlaid and above it. It is said Constantine saw this symbol prior to converting to Christianity (see History and origins section below). Another ancient symbol is an anchor, which denotes faith and can incorporate a cross within its design.
History and origins

In the mid-first century, Christianity spread beyond its Jewish origins under the leadership of the Apostles, especially Peter and Paul. Within a generation an episcopal hierarchy can be seen, and this would form the structure of the Church.Christianity spread east to Asia and throughout the Roman Empire, despite persecution by the Roman Emperors until its legalization by Emperor Constantine in 313. During his reign, questions of orthodoxy lead to the convocation of the first Ecumenical Council, that of Nicaea.
In 391 Theodosius I established Nicene Christianity as the official and, except for Judaism, only legal religion in the Roman Empire. Later, as the political structure of the empire collapsed in the West, the Church assumed political and cultural roles previously held by the Roman aristocracy. Eremitic and Coenobitic monasticism developed, originating with the hermit St Anthony of Egypt around 300. With the avowed purpose of fleeing the world and its evils in contemptu mundi, the institution of monasticism would become a central part of the medieval world.
Christianity became the established church of the Axumite Kingdom (presently encompassing Eritrea and Northern Ethiopi ) under king Ezana in the 4th century through the efforts of a Syrian Greek named Frumentius, known in Ethiopia as Abba Selama, Kesaté Birhan ("Father of Peace, Revealer of Light"), thus making Ethiopia one of the first christian state even before most of Europe. As a youth, Frumentius had been shipwrecked with his brother Aedesius on the Eritrean coast. The brothers managed to be brought to the royal court, where they rose to positions of influence and converted Emperor Ezana to Christianity, causing him to be baptised. Ezana sent Frumentius to Alexandria to ask the Patriarch, St. Athanasius, to appoint a bishop for Ethiopia. Athanasius appointed Frumentius himself, who returned to Ethiopia as Bishop with the name of Abune Selama.
During the Migration Period of Late Antiquity, various Germanic peoples adopted Christianity. Meanwhile, as western political unity dissolved, the linguistic divide of the Empire between Latin-speaking West and the Greek-speaking East intensified. By the Middle Ages distinct forms of Latin and Greek Christianity increasingly separated until cultural differences and disciplinary disputes finally resulted in the Great Schism (conventionally dated to 1054), which formally divided Christendom into the Catholic west and the Orthodox east. Western Christianity in the Middle Ages was characterized by cooperation and conflict between the secular rulers and the Church under the Pope, and by the development of scholastic theology and philosophy.
Beginning in the 7th century, Muslim rulers began a long series of military conquests of Christian areas, and it quickly conquered areas of the Byzantine Empire in Asia Minor, Palestine, Syria, Egypt, and North Africa, and even captured southern Spain. Numerous military struggles followed, including the Crusades, the Spanish Reconquista, the Fall of Constantinople and the aggression of the Turks.
In the early sixteenth century, increasing discontent with corruption and immorality among the clergy resulted in attempts to reform the Church and society. The Protestant Reformation began after Martin Luther published his 95 theses in 1517, whilst the Roman Catholic Church experienced internal renewal with the Counter-Reformation and the Council of Trent (1545-1563). During the following centuries, competition between Catholicism and Protestantism became deeply entangled with political struggles among European states. Meanwhile, partly from missionary zeal, but also under the impetus of colonial expansion by the European powers, Christianity spread to the Americas, Oceania, East Asia, and sub-Saharan Africa.
In the Modern Era, Christianity was confronted with various forms of skepticism and with certain modern political ideologies such as liberalism, nationalism, and socialism. This included the anti-clericalism of the French Revolution, the Spanish Civil War, and general hostility of Marxist movements, especially the Russian Revolution.
Persecution
Christians have frequently suffered from persecution. Starting with Jesus, the early Christian church was persecuted by state and religious establishments from its earliest beginnings. Notable early Christians such as Stephen, eleven of the Apostles as well as Paul died as martyrs according to tradition. Systematic Roman persecution of Christians culminated in the Great Persecution of Diocletian and ended with the Edict of Milan. Persecution of Christians persisted or even intensified in other places, such as in Sassanid Persia. Later Christians living in Islamic countries were subjected to various legal restrictions, which included taxation and a ban on building or repairing churches. Christians at times also suffered violent persecution or confiscation of their property
There was persecution of Christians during the French Revolution (see Dechristianisation of France during the French Revolution). State restrictions on Christian practices today are generally associated with those authoritarian governments which either support a majority religion other than Christianity (as in Muslim states), or tolerate only churches under government supervision, sometimes while officially promoting state atheism (as in North Korea). The People's Republic of China allows only government-regulated churches and has regularly suppressed house churches and underground Catholics. The public practice of Christianity is outlawed in Saudi Arabia. Areas of persecution include other parts of the Middle East, the Sudan, and Kosovo.
Christians have also been perpetrators of persecution against other religions and other Christians. Christian mobs, sometimes with government support, destroyed pagan temples and oppressed adherents of paganism (such as the philosopher Hypatia of Alexandria, who was murdered by a Christian mob). Also, Jewish communities have periodically suffered violence at Christian hands. Christian governments have suppressed or persecuted groups seen as heretical, later in cooperation with the Inquisition. Denominational strife escalated into religious wars. Witch hunts, carried out by secular authorities or popular mobs, were a frequent phenomenon in parts of early modern Europe and, to a lesser degree, North America.
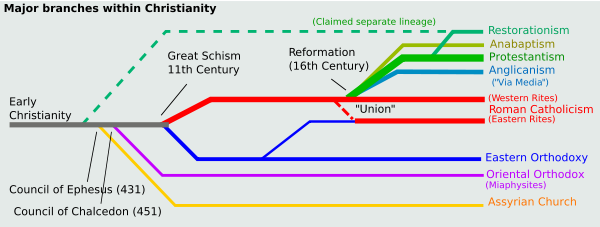
Christian divisions
There is a diversity of doctrines and practices among groups calling themselves Christian. These groups are sometimes classified under denominations, though for theological reasons many groups reject this classification system. Christianity may be broadly represented as being divided into three main groupings:
- Roman Catholicism: The Roman Catholic Church, the largest single body, includes the Latin Rite and totals more than 1 billion baptized members.
- Eastern Christianity: Eastern Orthodox Churches, Oriental Orthodox Churches, the 100,000 member Assyrian Church of the East, and others with a combined membership of more than 300 million baptized members.
- Anglicanism: The Anglican Communion is a group of Anglican and Episcopal Churches that are descended from the Church of England. Most Anglicans don't consider themselves Protestant or Catholic but believe that the Church of England always existed and wasn't formed during the Reformation but rather broke away from the Church of Rome.
- Protestantism: Groups such as Lutherans, Reformed/ Presbyterians, Congregational/ United Church of Christ, Evangelical, Charismatic, Baptists, Methodists, Nazarenes, Anabaptists, Seventh-day Adventists and Pentecostals. The oldest of these separated from the Roman Catholic Church in the 16th century Protestant Reformation, followed in many cases by further divisions. Estimates of the total number of Protestants are very uncertain, partly because of the difficulty in determining which denominations should be placed in this category, but it seems to be unquestionable that Protestantism is the second major branch of Christianity (after Roman Catholicism) in number of followers.
Some Protestants identify themselves simply as Christian, or born-again Christian; they typically distance themselves from the confessionalism of other Protestant communities by calling themselves "non-denominational" — often founded by individual pastors, they have little affiliation with historic denominations. Finally, various small communities, such as the Old Catholic and Independent Catholic Churches, are similar in name to the Roman Catholic Church, but are not in communion with the See of Rome (the Old Catholic church is in communion with the Anglican Church).
Restorationists, are historically connected to the Protestant Reformation, do not usually describe themselves as "reforming" a Christian Church continuously existing from the time of Jesus, but as restoring the Church that they believe was lost at some point. Restorationists include Churches of Christ with 2.6 million members, Disciples of Christ with 800,000 members, The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints with 12 million members, and Jehovah’s Witnesses with 6.6 million members. Though Restorationists have some superficial similarities, their doctrine and practices vary significantly.
Mainstream Christianity
Mainstream Christianity is a widely used term, used to refer to collectively to the common views of major denominations of Christianity (such as Roman Catholicism, Protestantism, Anglicanism, Orthodox Christianity) as against the particular tenets of other sects or Christian denomination. The context is dependent on the particular issues addressed, but usually contrasts the orthodox majority view against heterodox minority views. In the most common sense, "mainstream" refers to Nicene Christianity, or rather the traditions which continue to claim adherence to the Nicene Creed.
Some groups identifying themselves as Christian deviate from the tenets considered basic by most Christian organizations. These groups are often considered heretical, or even non-Christian, by many mainstream Christians. This is particularly true of non-trinitarians.
Ecumenism
Most churches have long expressed ideals of being reconciled with each other, and in the 20th Century Christian ecumenism advanced in two ways. One way was greater cooperation between groups, such as the Edinburgh Missionary Conference of Protestants in 1910, the Justice, Peace and Creation Commission of the World Council of Churches founded in 1948 by Protestant and Orthodox churches, and similar national councils like the National Council of Churches in Australia which also includes Roman Catholics.
The other way was institutional union with new United and uniting churches. Congregationalist, Methodist, and Presbyterian churches united in 1925 to form the United Church of Canada and in 1977 to form the Uniting Church in Australia. The Church of South India was formed in 1947 by the union of Anglican, Methodist, Congregationalist, Presbyterian, and Reformed churches.
Steps towards union on a global level have also been taken in 1965 by the Catholic and Orthodox churches mutually revoking the excommunications that marked their Great Schism in 1054; the Anglican Roman Catholic International Commission (ARCIC) working towards full communion between those churches since 1970; and the Lutheran and Catholic churches signing The Joint Declaration on the Doctrine of Justification in 1999 to address conflicts at the root of the Protestant Reformation. In 2006 the Methodist church also adopted the declaration.